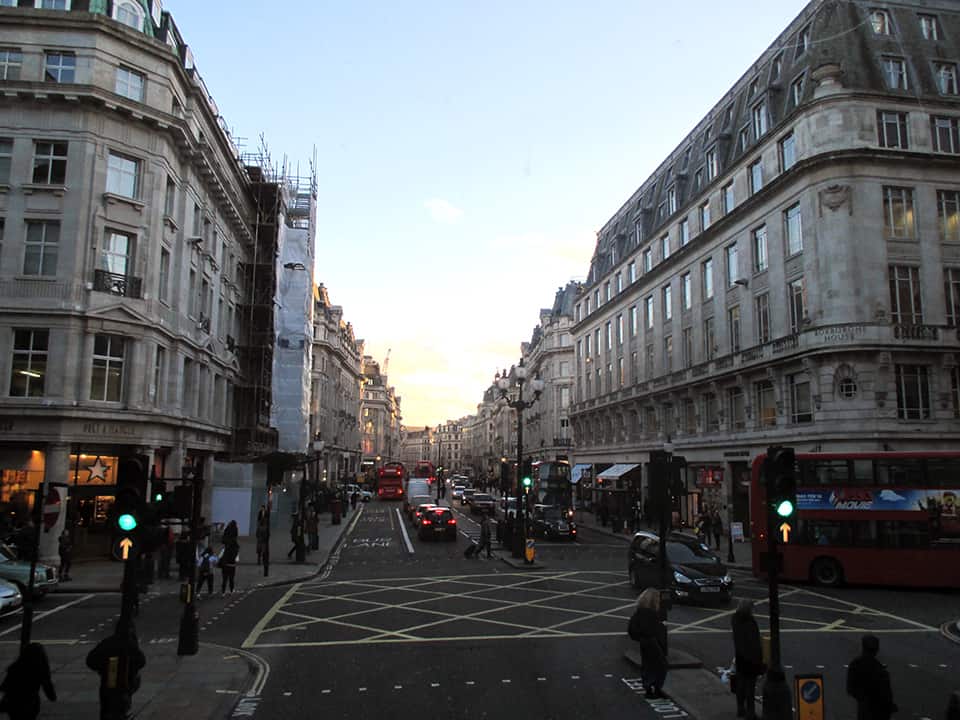
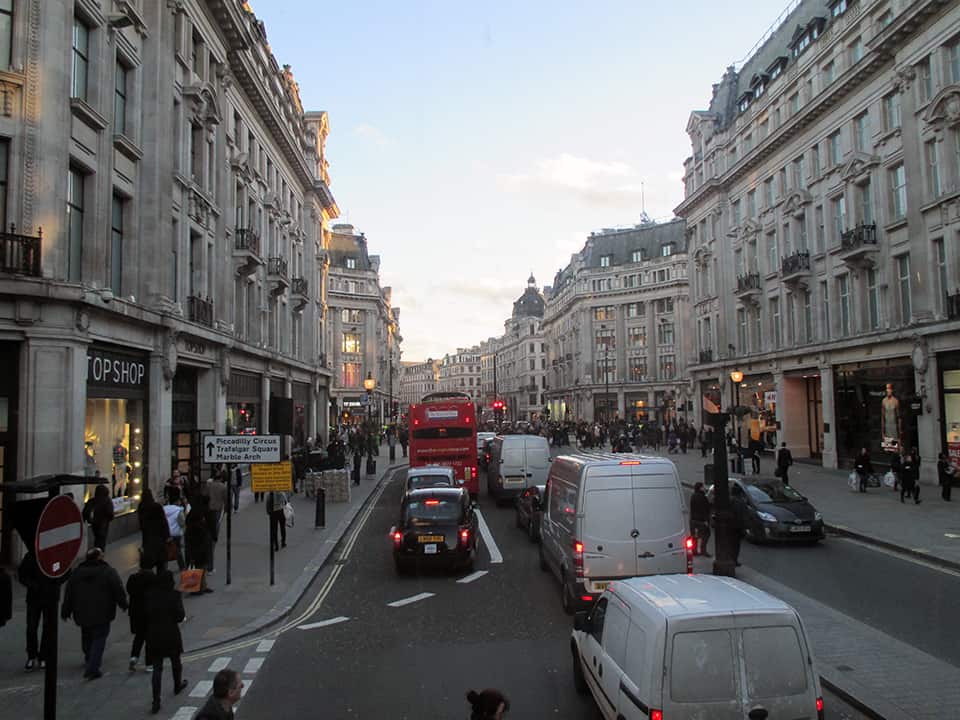
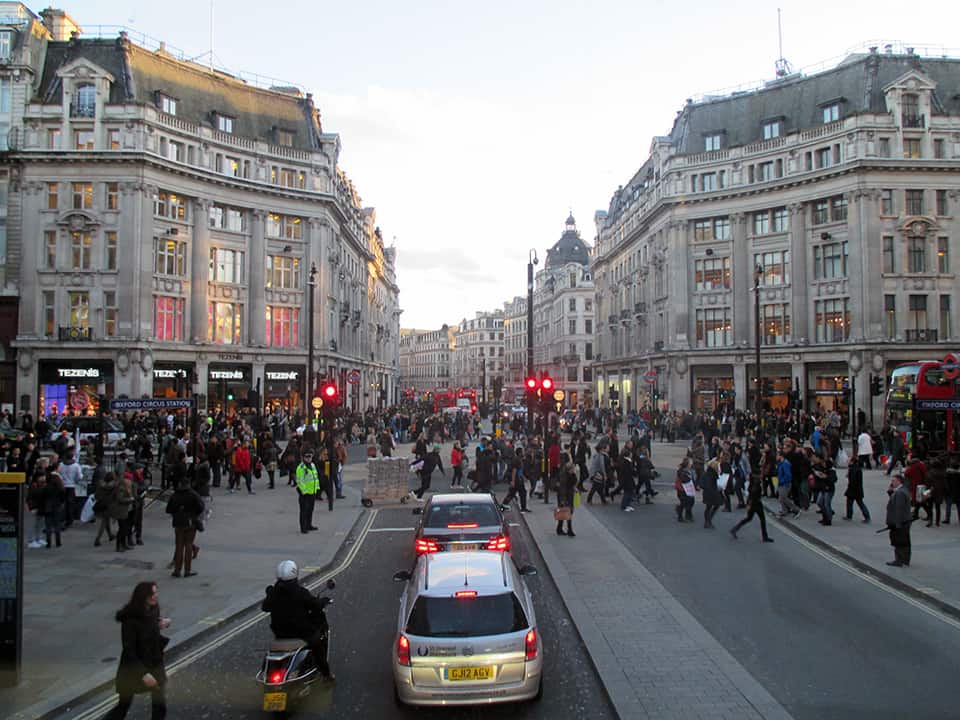
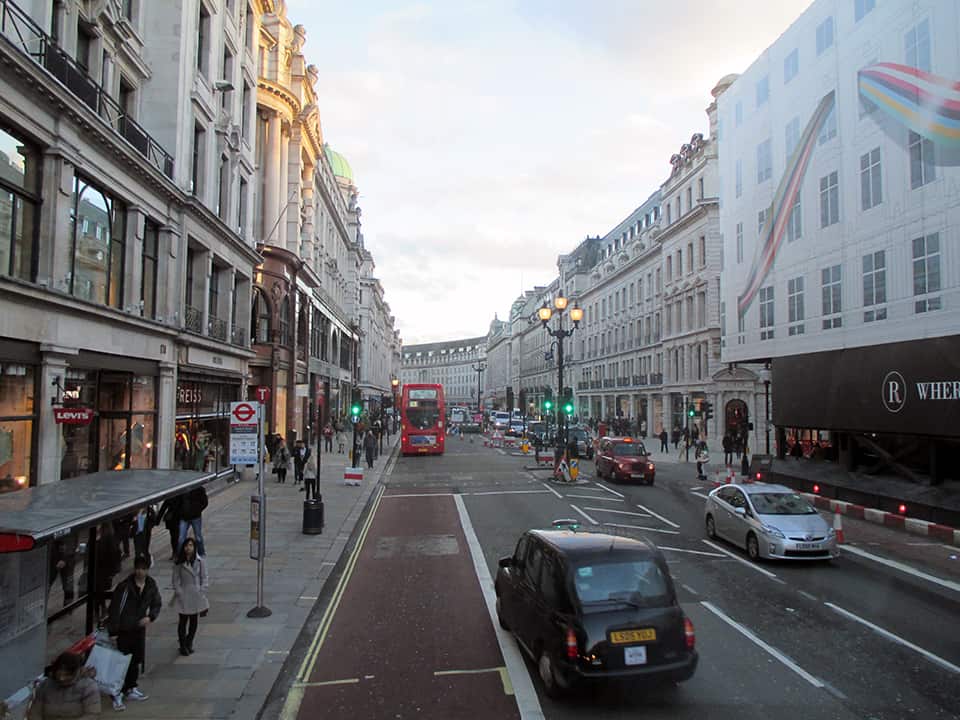
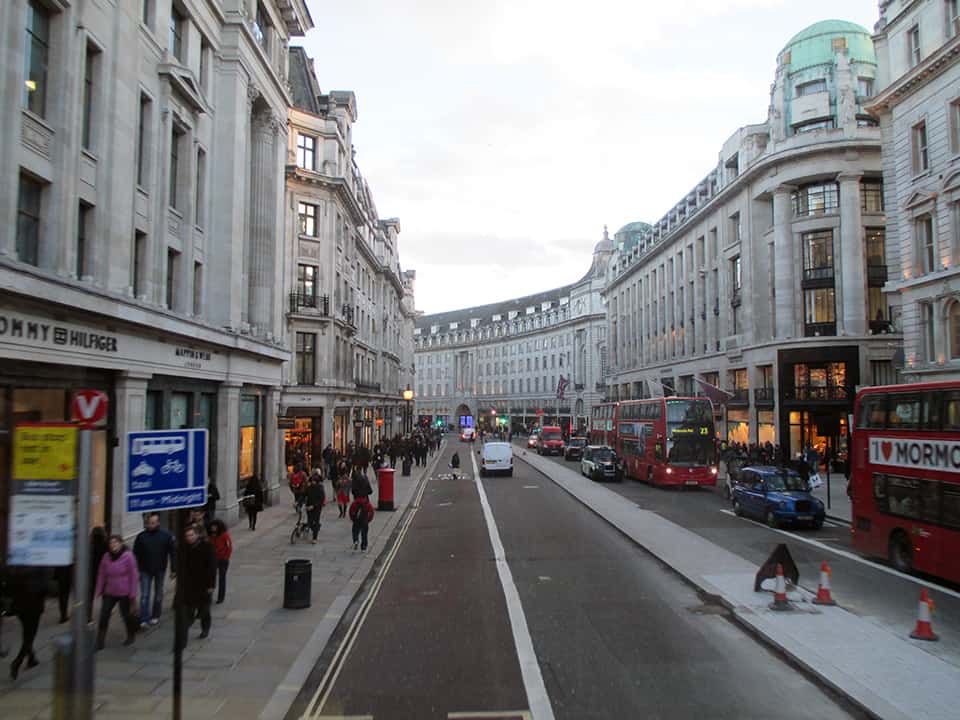
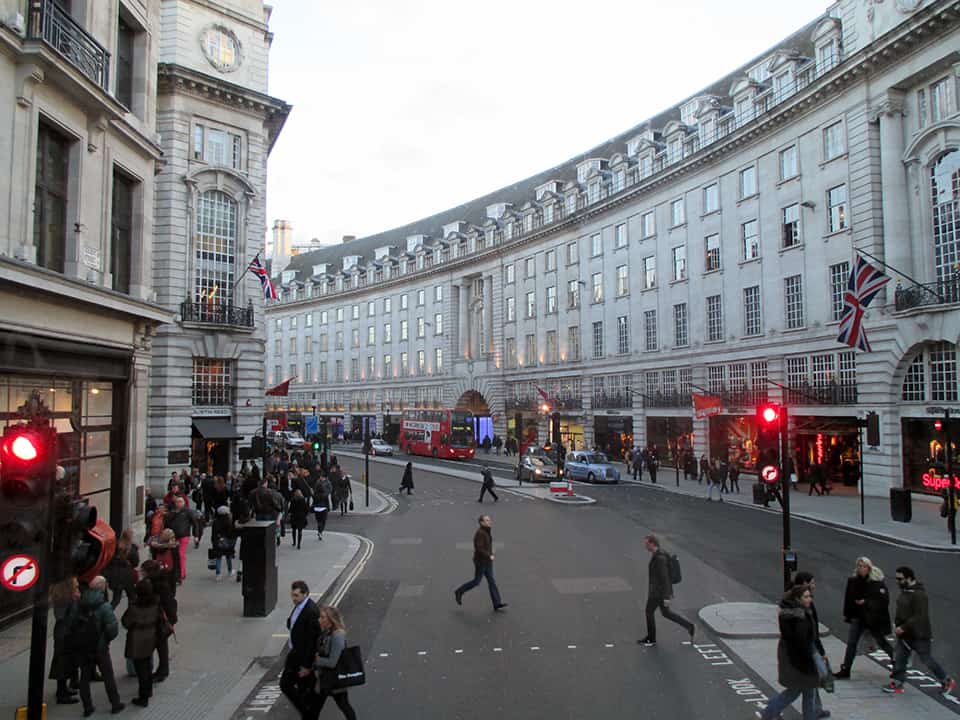
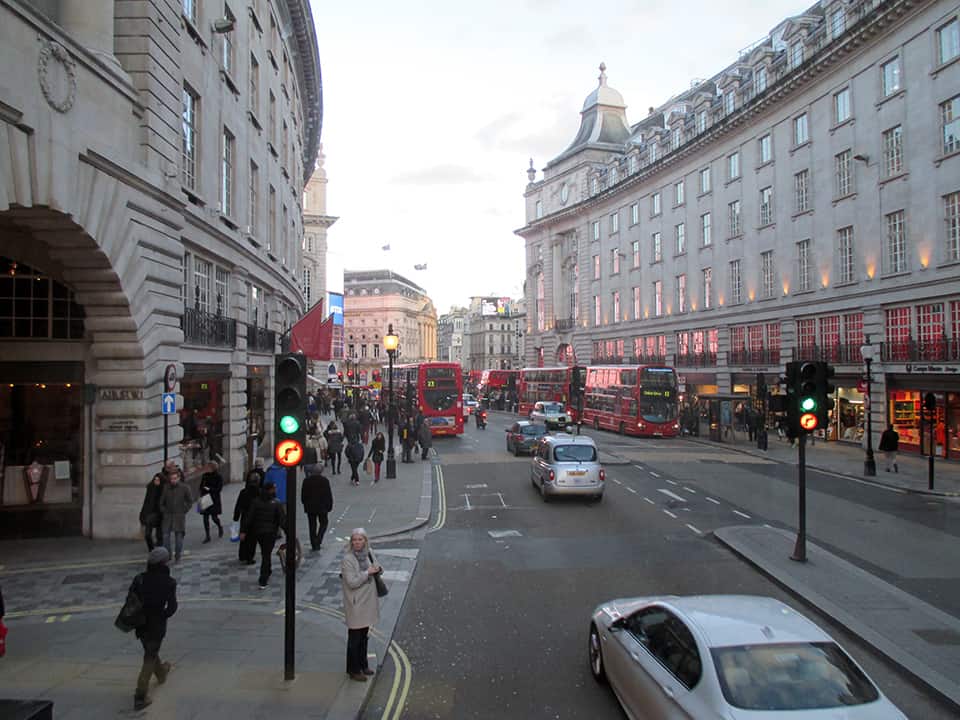
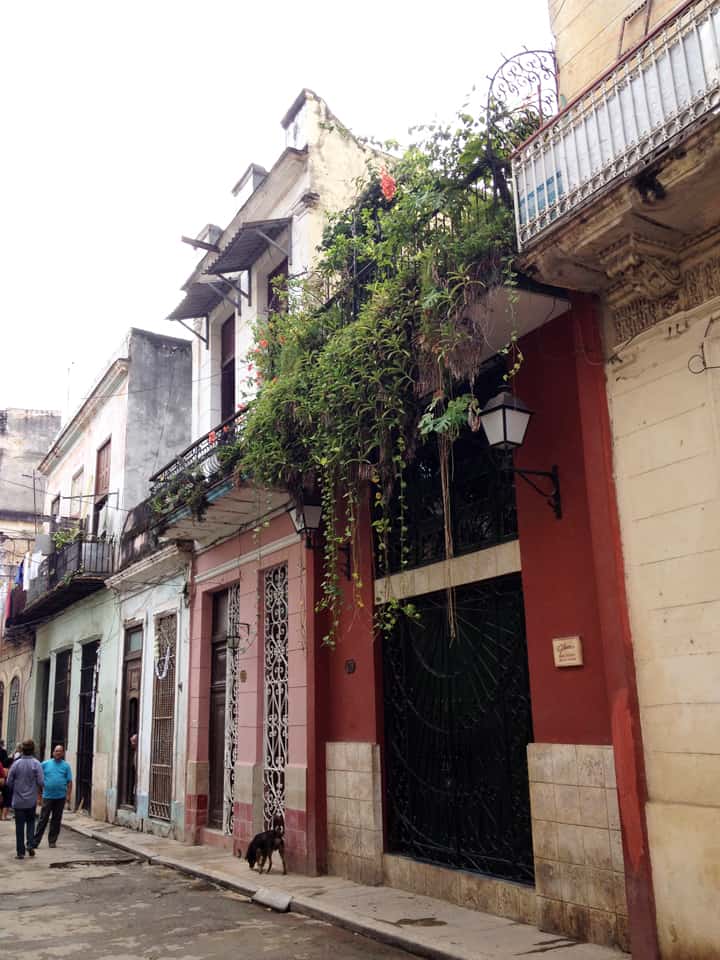
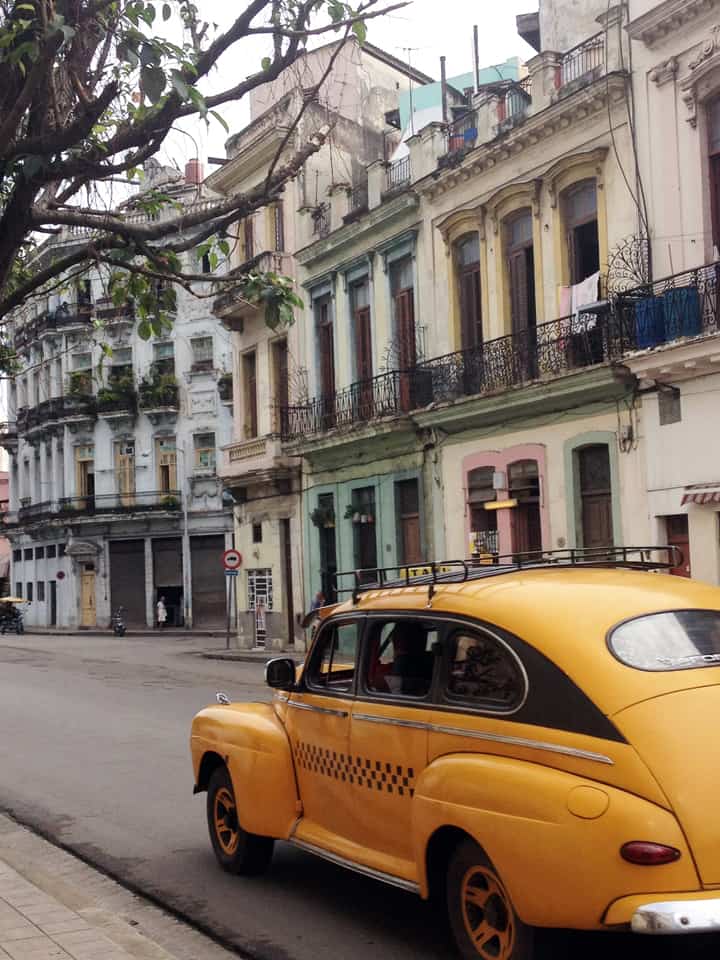
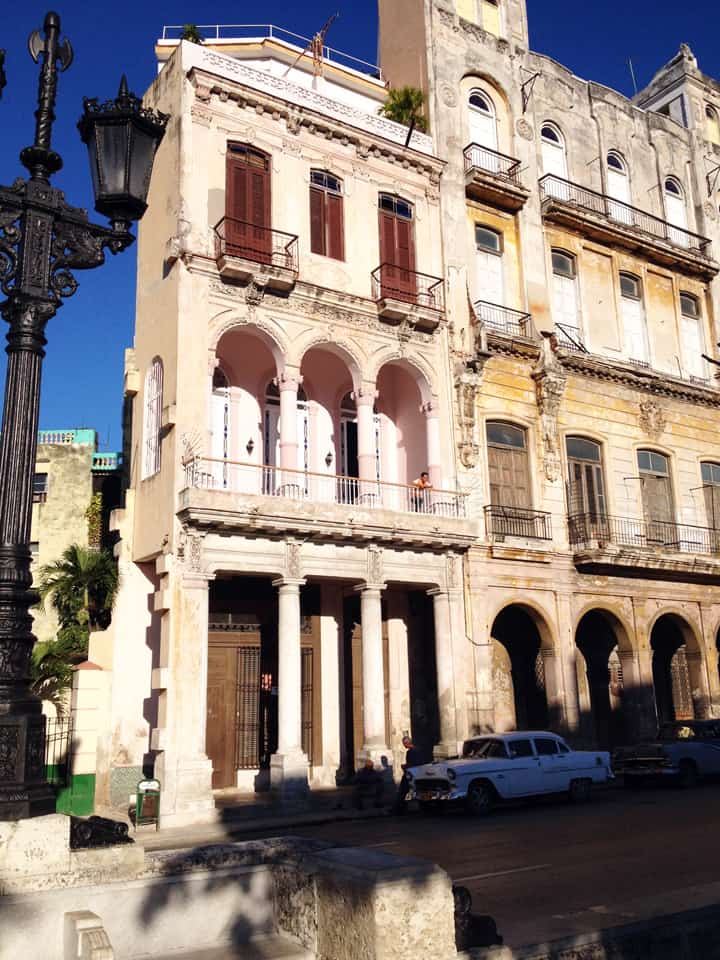
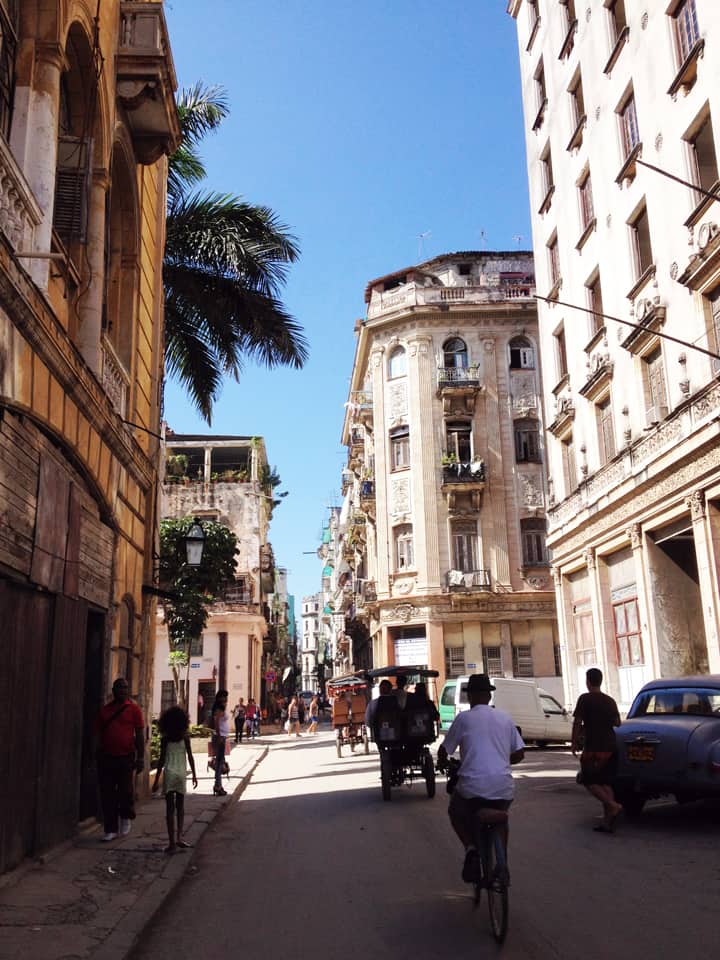
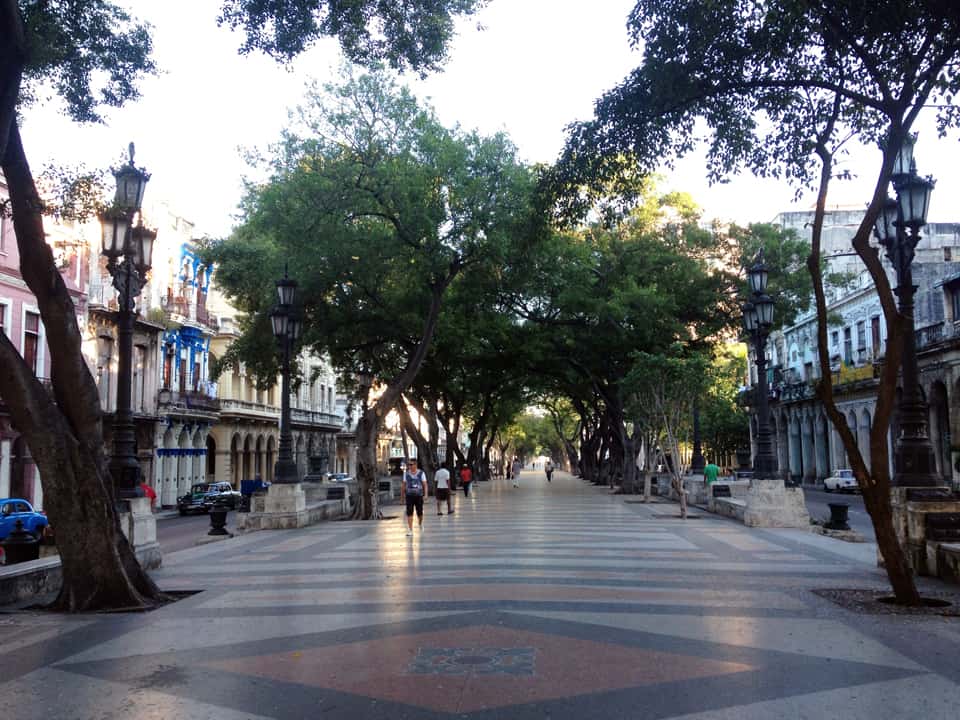
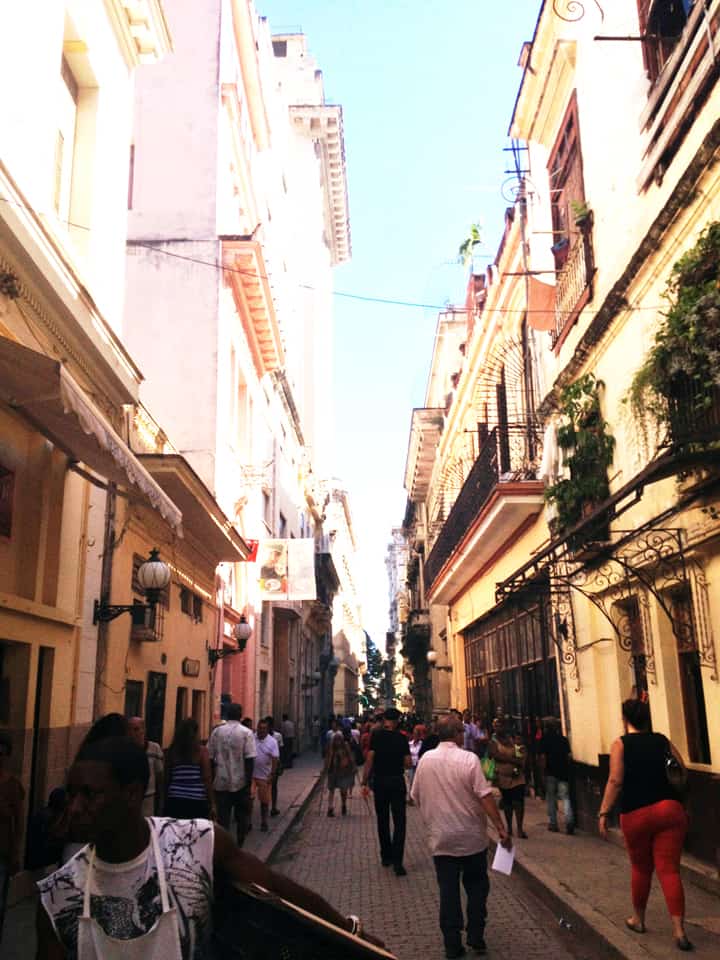
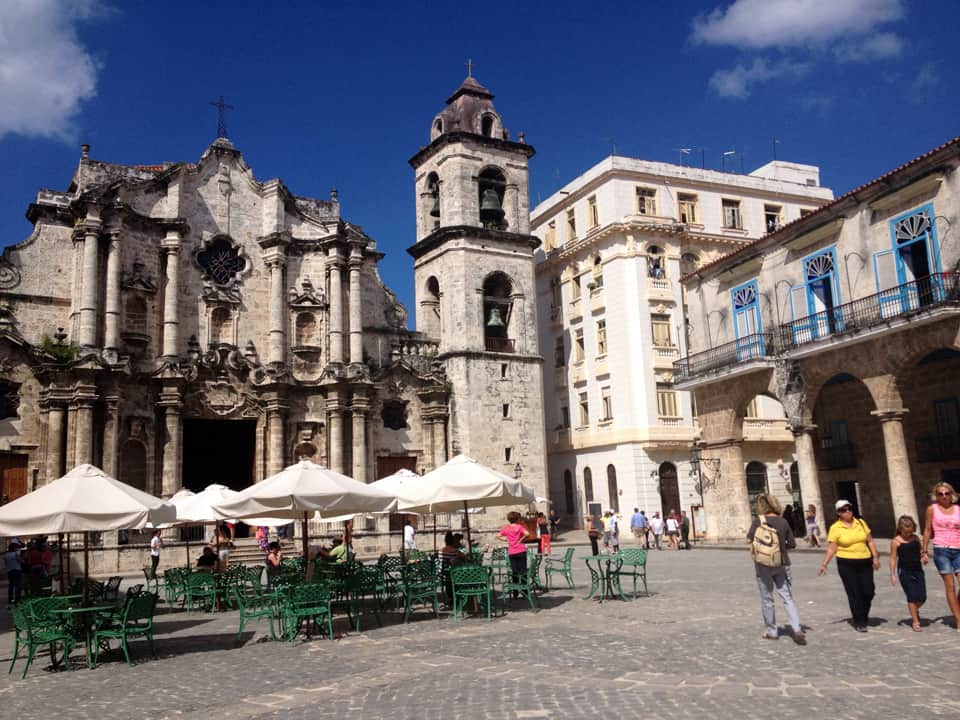
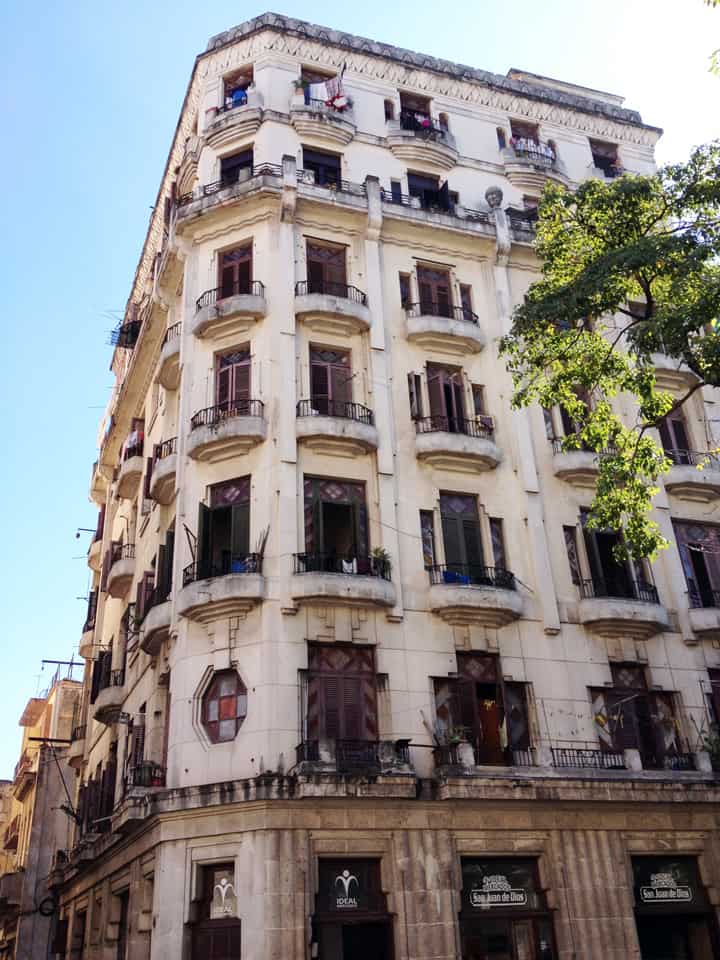
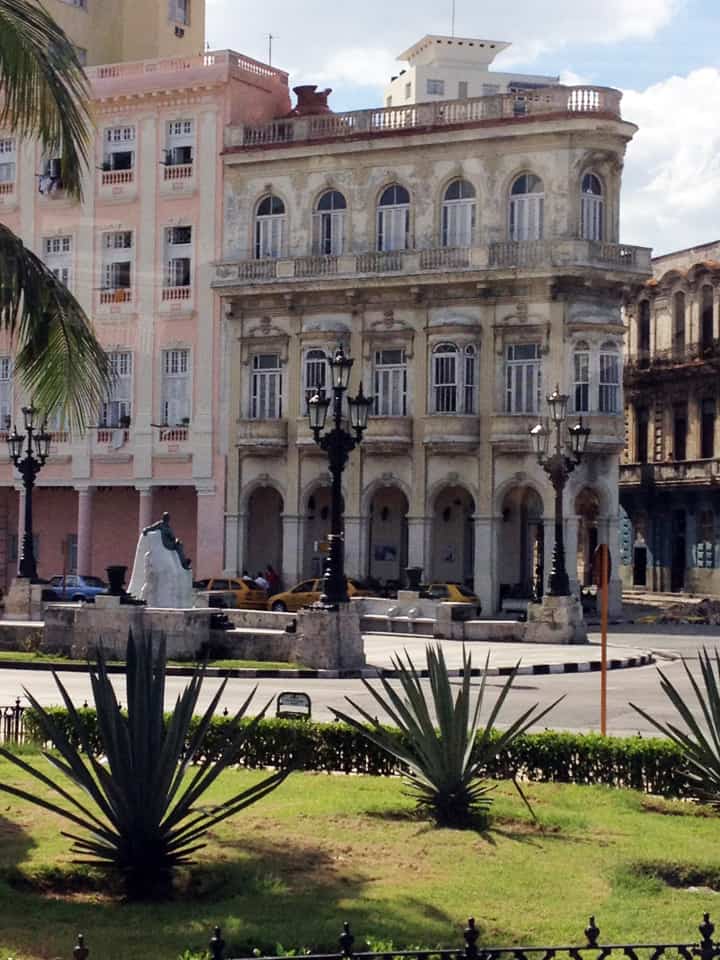
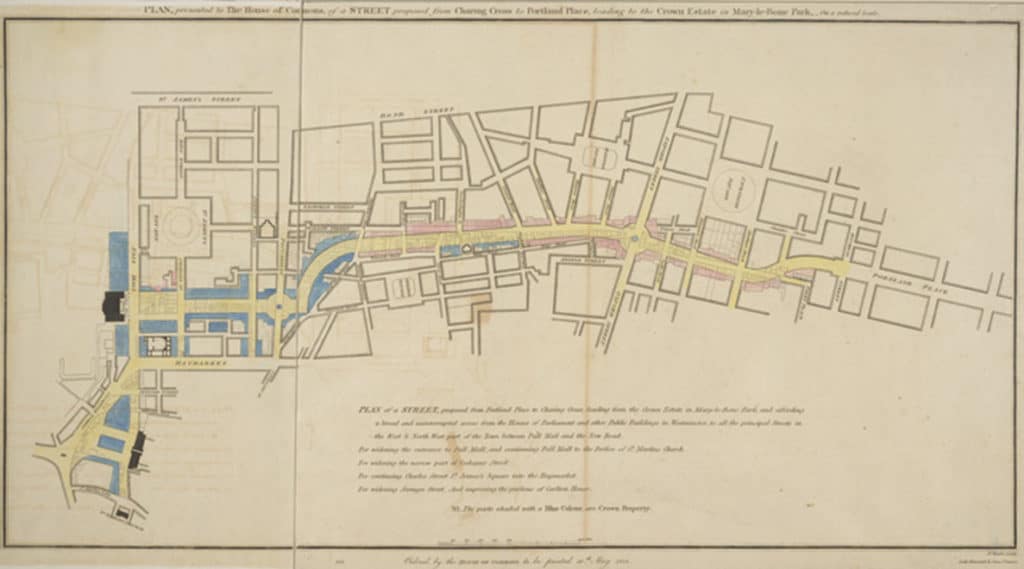
It has been said that ‘Savannah is all about its squares.’ This is inaccurate. The spatial logic of Savannah is all about the historical loading of front doors along east-west streets in the ward plan. This generates a spatial hierarchy in the plan between ‘outsiders’ (i.e. visitors) principally using north-south streets to enter the town (historically from the port, later via vehicular traffic) before assimilating along the east-west streets primarily used by ‘insiders’ (i.e. residents) (Anderson, 1986 and 1993; Kostof, 1991; Major, 2001 and 2014).
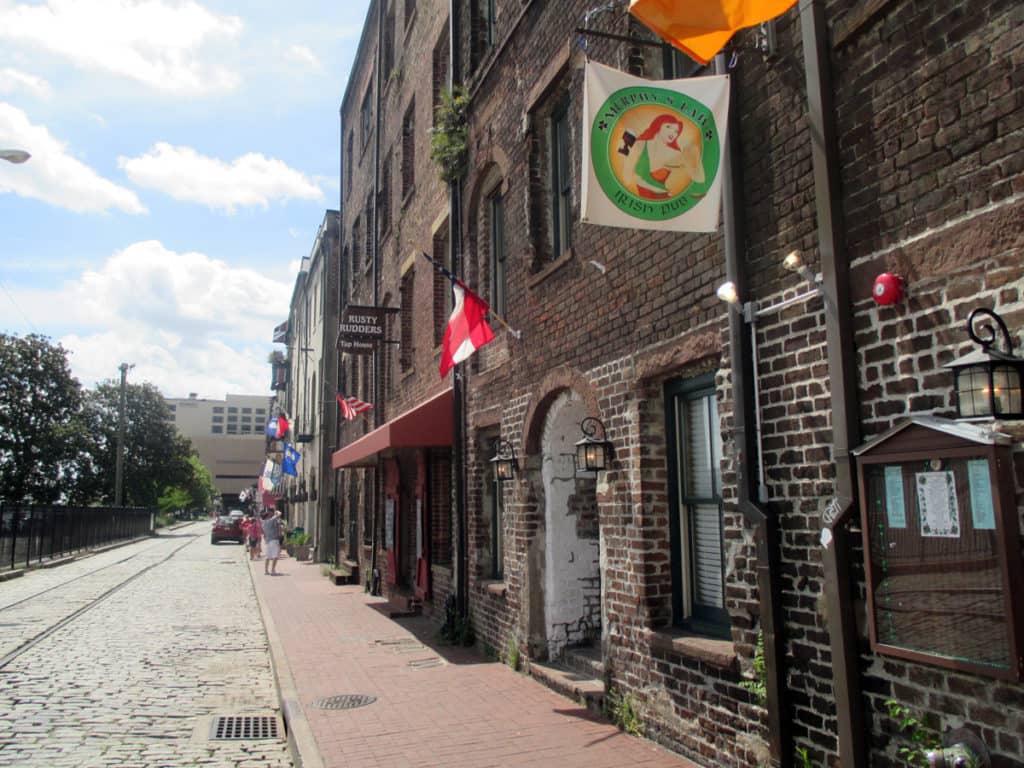
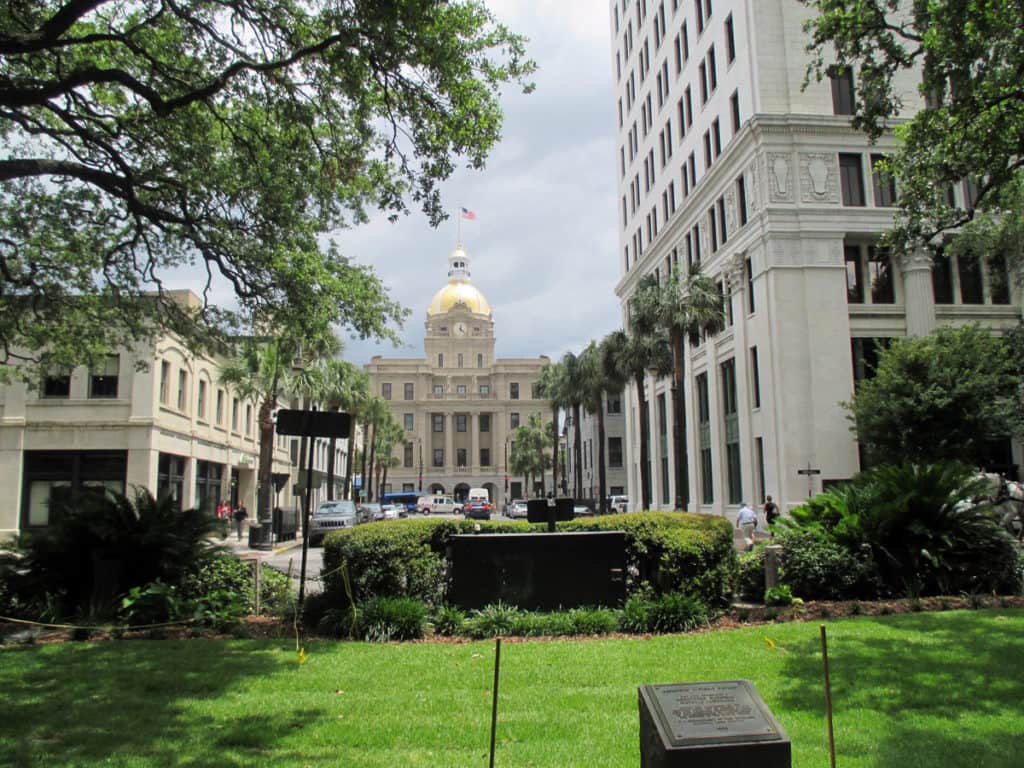
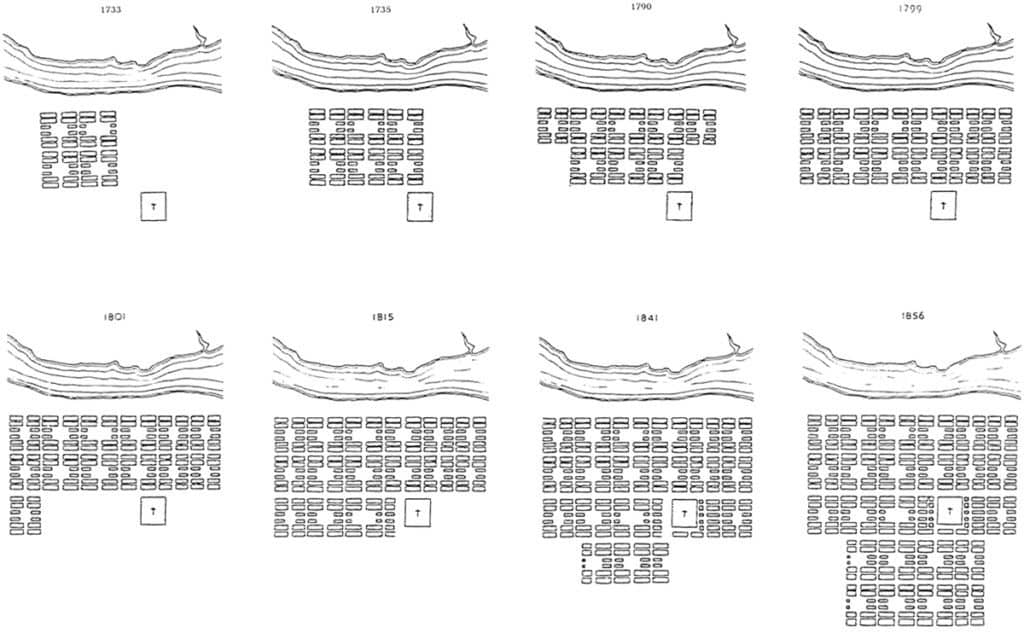






The spatial logic of the ward plan is imminently serviceable for managing moving traffic, treating most squares as enlarged roundabouts and filtering through traffic mostly along north-south streets such as this one. Over time, constitution (i.e. dwelling entrances) has emerged in a spotty fashion along these north-south streets but not enough (to date) to deteriorate the logic of loading front doors along east-west streets.
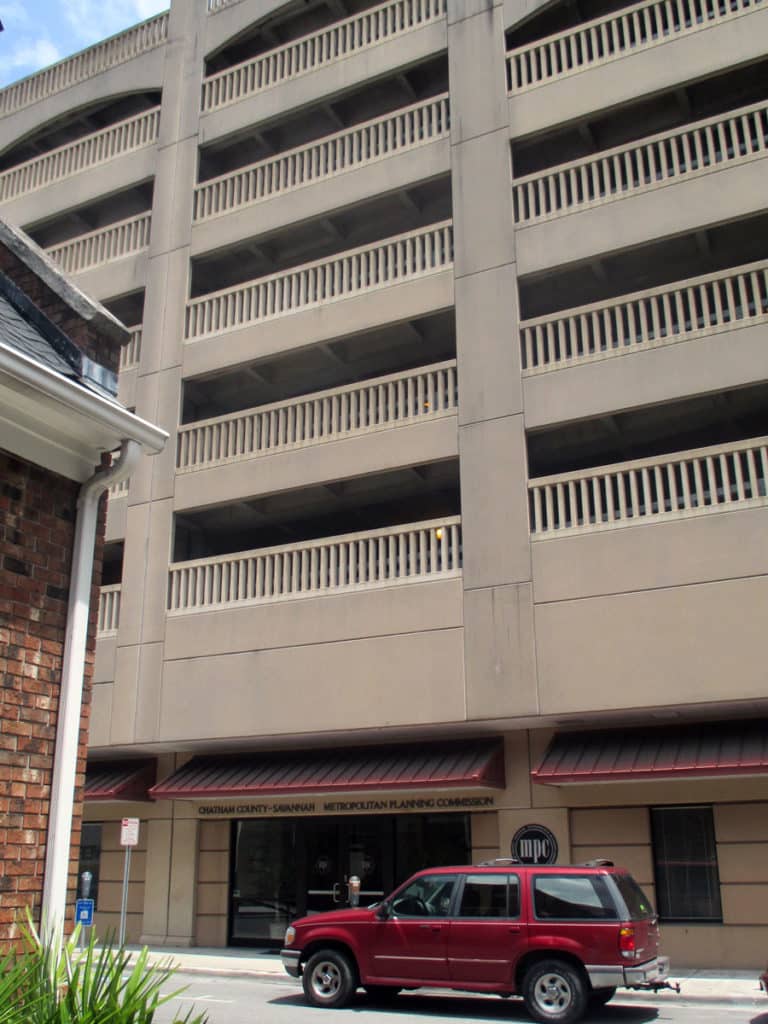

Despite this, Savannah’s ward plan is suffering under the weight of storing parked vehicles. There are parking garages located on at least four of the squares and two sides of Orleans Square is constituted by surface parking for the convention center. The wall constructed to ‘hide’ this surface parking does nothing to support the functioning of the ward plan or Orleans Square itself. This photo shows the Chatham County-Savannah Metropolitan Planning Commission offices occupying a ground level retail space (not a bad idea but poorly designed frontage) on Oglethorpe Square at the base of a seven-story parking garage (metaphorically-speaking, being crushed under the weight of parked vehicles).
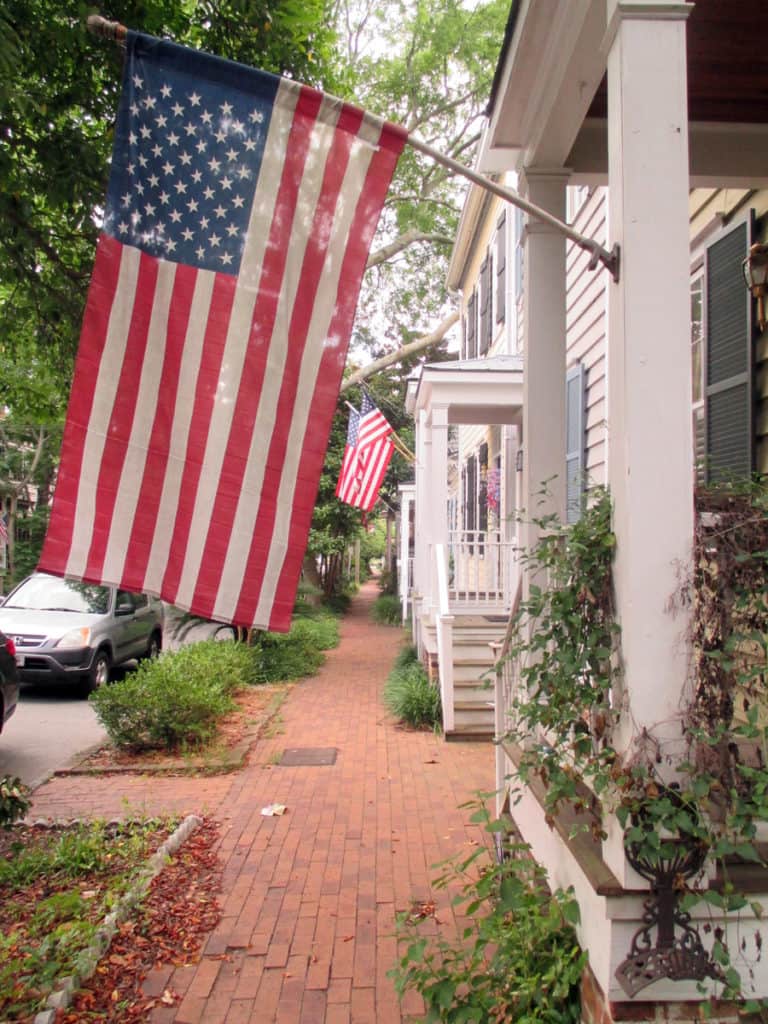
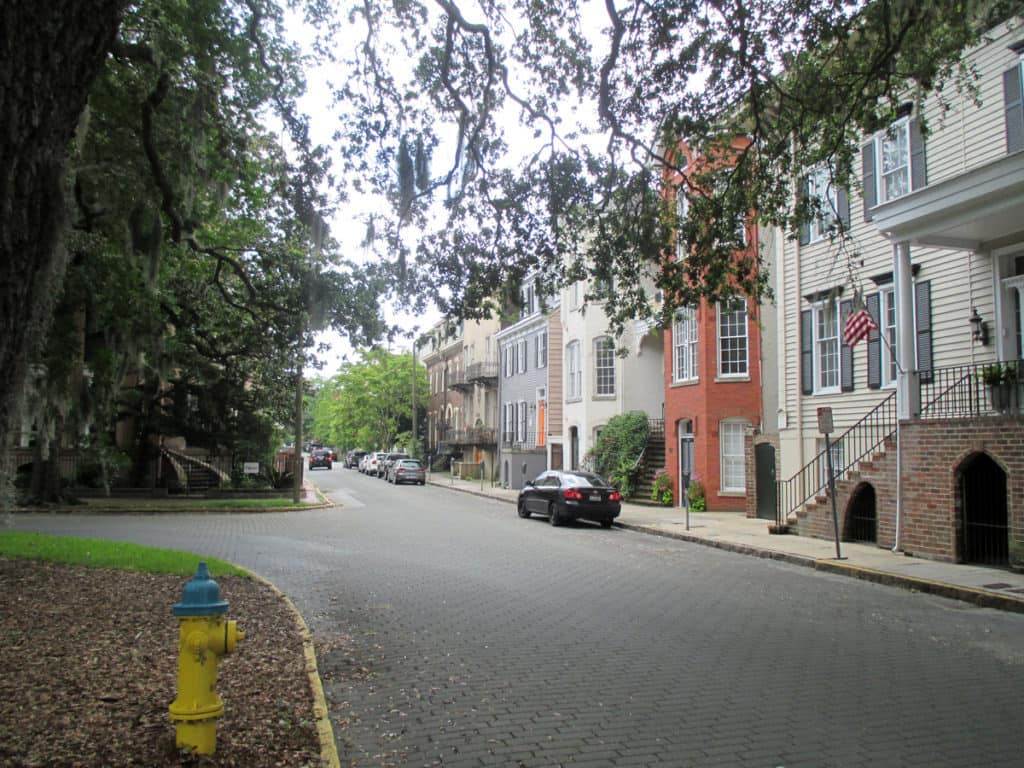
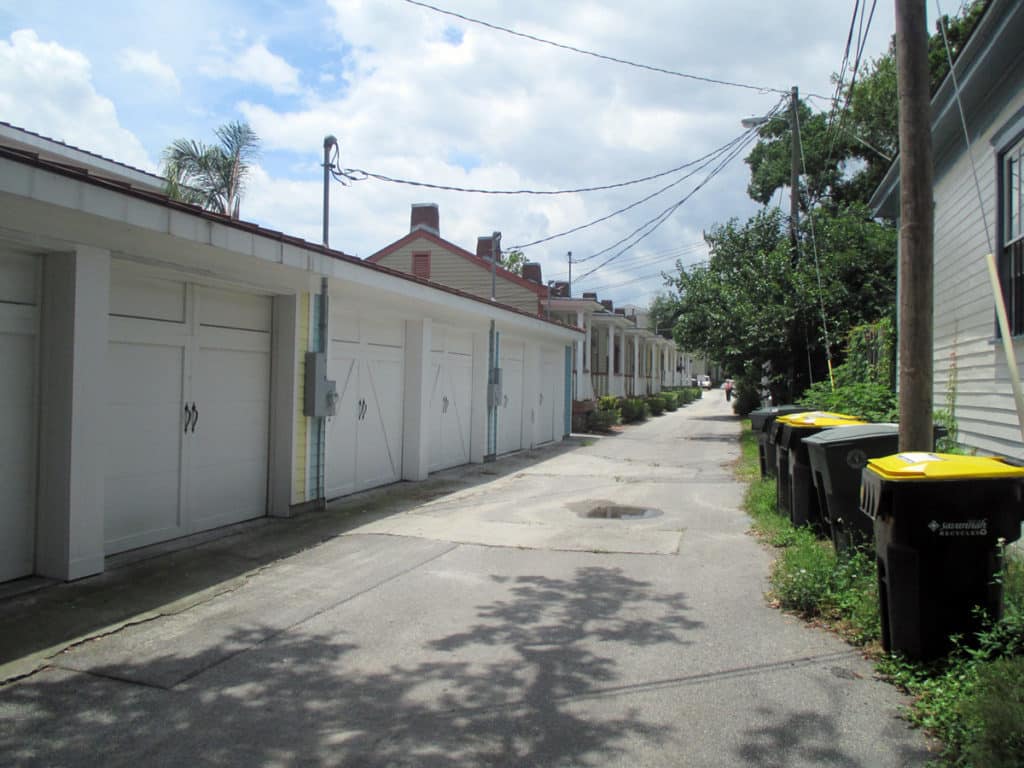



Some modern in-fill development adheres to the nuances of how Savannah’s ward plan was historically designed to function (front doors loaded on this east-west street in the development in the background) whereas some actively retards that functioning (garages loaded on east-west street in the development in the foreground, turning this portion of the space into an alleyway with trash cans).
References
Anderson, Stanford. 1993. “Savannah and the Issue of Precedent: City Plan as Resource”, Settlements in the Americas: Cross-Cultural Perspectives (Ed. Ralph Bennett). Newark: University of Delaware Press.
Anderson Stanford. 1986. “Studies towards an Ecological Model of Urban Environment”, On Streets (Ed. Stanford Anderson). Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press.
Kostof, Spiro. 1991. The City Shaped: Urban Patterns and Meaning Through History. London: Thames and Hudson, Ltd.
Major, Mark David. 2015. Relentless Magnificence: The American Urban Grid. Ph.D. Thesis. Copies available from University College London.
Major, Mark David. 2001. “When is a door more than a door? The role of constitution in strongly geometric configurations”, Third International Space Syntax Symposium Proceedings (Eds. J. Peponis, J. Wineman, S. Bafna), 37.1-37.14.
Reps, John W. 1965. The Making of Urban America: A History of City Planning in the United States. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.