“Leave them kids alone!
All in all it’s just another brick in the wall,
All in all you’re just another brick in the wall.”
— Another Brick in the Wall (Part 2), Pink Floyd
Urban Patterns | Nicosia, Cyprus
by Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A
Nicosia is the largest city on the island of Cyprus. It is located near the center of the Mesaoria plain on the banks of the River Pedieos. It is the capital and seat of government of the Republic of Cyprus. As such, it is the farthest southeast of all European Union member states’ capitals. It has been the capital of Cyprus since the 10th century. The Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot communities of Nicosia segregated into the south and north of the city respectively in 1963 following the outbreak of violence. This division became a militarized border between the Republic of Cyprus and Northern Cyprus after Turkey invaded the island in 1974, occupying the north of the island including northern Nicosia.

Today, the northern part of the city is the capital of Northern Cyprus, a state recognized only by Turkey, which is considered occupied Cypriot territory by the international community. Nicosia has been in continuous habitation since the beginning of the Bronze Age (i.e. over 4,5000 years) when the first inhabitants settled in the area. Nicosia later became a city-state known as Ledra or Ledrae, one of the twelve kingdoms of ancient Cyprus built by Achaeans after the end of the Trojan War. Remains of old Ledra today can be found in the Ayia Paraskevi hill in the southeast of the city (Source: Wikipedia).
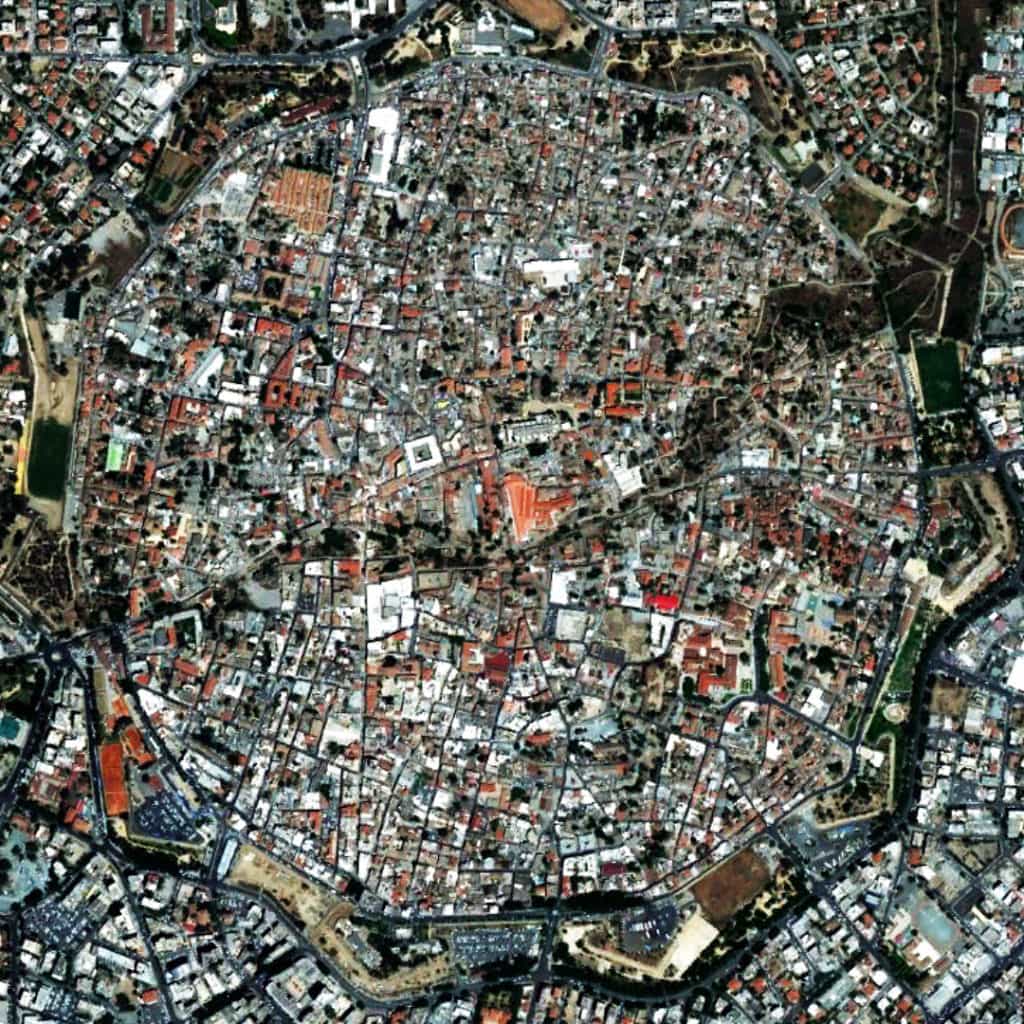
Nicosia, Cyprus has an interesting urban pattern for a variety of reasons. First, after the fall of the Berlin Wall, it is the only remaining divided city in the world (the demarcation is the “Green Line”, evident at the center of the above satellite image from 8,000 feet) between the Turkish north and the Greek south. Second, the city is characterized by a deformed grid layout. However, within the walls of the old city, the pattern of streets in the Turkish north is more characteristic of Middle Eastern cities where smaller block sizes and narrow street widths serve to complicate continuous lines of sights. In the Greek south, street widths are wider, blocks are larger, and the layout is more geometric in nature. This indicates a clear distinction in the social construction of space by two cultures (predominantly Turkish/Islāmic in the north and Greek/Orthodox Christian in the south). However, as interesting as this is, it is not the most remarkable thing about Nicosia. When you zoom out to encompass more of the surrounding urban context outside the walls of the old city (see header image from 15,000 feet), the deformed grid of the city is everywhere more characterized (in relative terms by comparison to the street pattern within the old city walls) by wider and straighter streets, larger blocks, and a more geometrical layout as a whole; again, more so to the south than the north. This ably demonstrates the necessity of urban functionality in overcoming the social imprint of space in order to better mediate the relationship between city center and the ever-expanding edges of that city.
(Updated: April 19, 2017)
Urban Patterns is a series of posts from The Outlaw Urbanist presenting interesting examples of terrestrial patterns shaped by human intervention in the urban landscape over time.


