“Barcelona is a very old city (where) you can feel the weight of history; it is haunted by history. You cannot walk around it without perceiving it.”
— Carlos Ruiz Zafon, Spanish novelist
“Barcelona – Such a beautiful horizon,
Barcelona – Like a jewel in the sun,
Por ti seré gaviota de tu bella mar.”
— Barcelona, Freddie Mercury
Urban Patterns | Barcelona, Spain
by Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A
Barcelona is the capital city of the autonomous community of Catalonia in the Kingdom of Spain, as well as the country’s second most populous municipality, with a population of 1.6 million within city limits. Its urban area extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of around 4.7 million people, being the sixth-most populous urban area in the European Union after Paris, London, Madrid, the Ruhr area and Milan. It is the largest metropolis on the Mediterranean Sea, located on the coast between the mouths of the rivers Llobregat and Besòs, and bounded to the west by the Serra de Collserola mountain range, the tallest peak of which is 512 meters (1,680 feet) high. The origins of Barcelona are shrouded in legend. However, around 15 BC the Romans re-planned the town as a castrum (Roman military camp) centered on the Mons Taber, a little hill near Plaça de Sant Jaume (Source: Wikipedia).
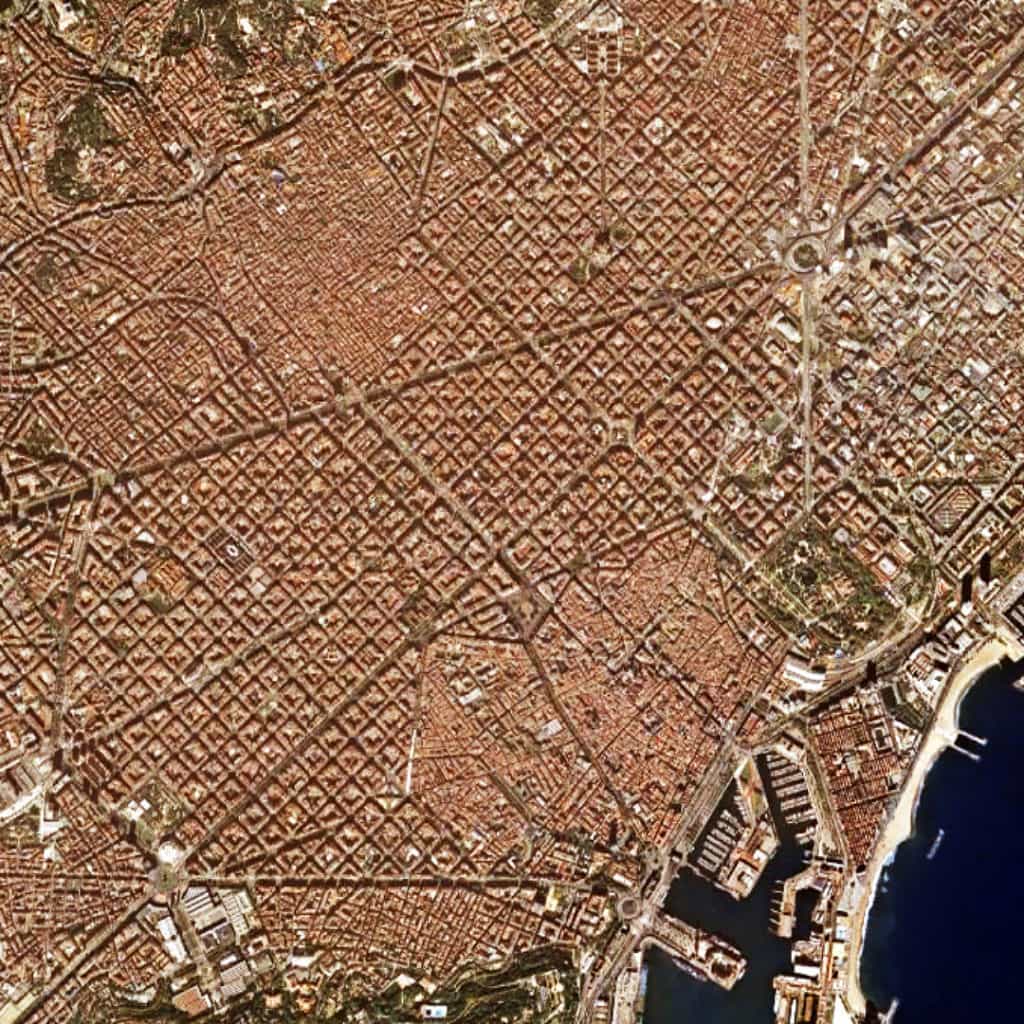

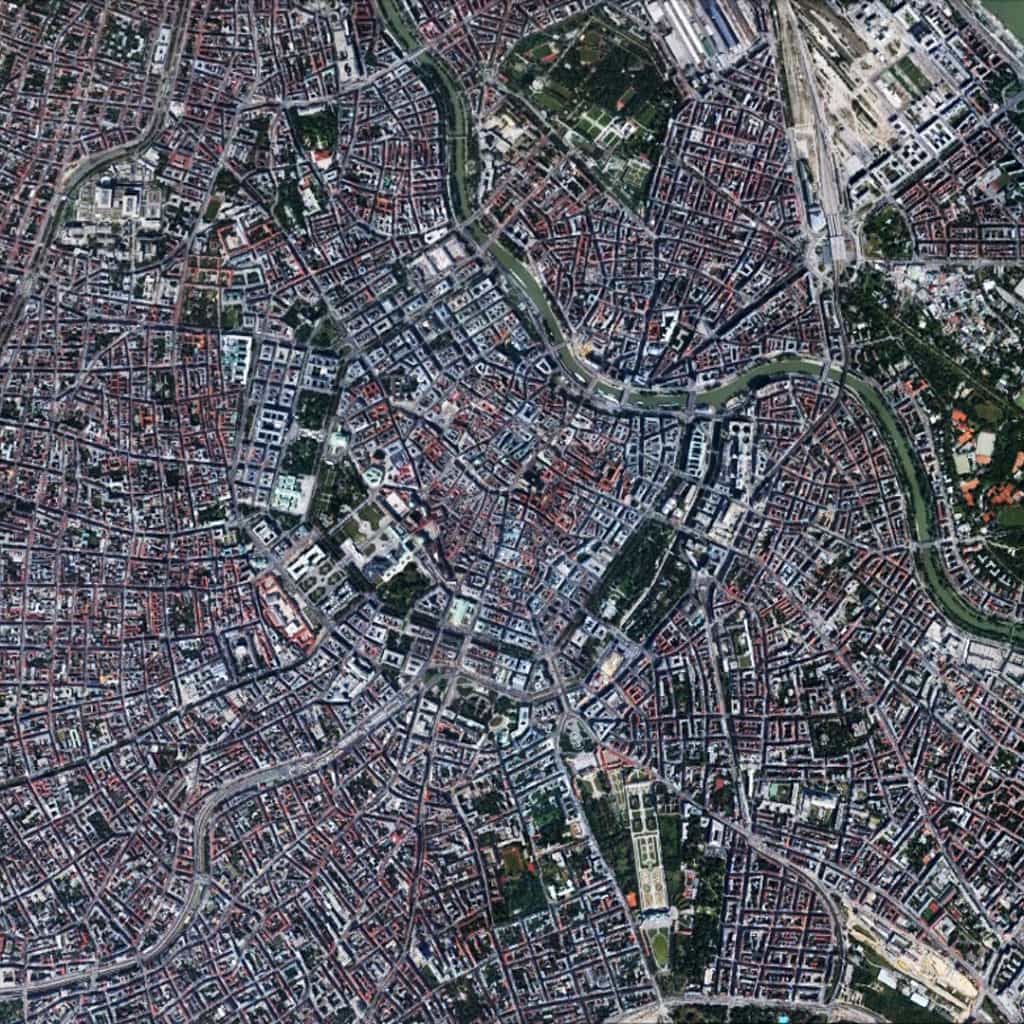
In the main, the urban pattern of Barcelona is defined by three distinctive components. The oldest part of the city called the “Gothic Quarter” has a deformed grid pattern (originally within fortifications that later became the alignment of streets) characterized by small streets and blocks (visible center right near the bottom of the above image). Despite this, the Gothic Quarter is well-connected into the larger city by the Via Laietana (running southeast-to-northwest in the northern portion of the Gothic Quarter) and La Rambla (more or less paralleling Via Laietana further to the south). The majority of Barcelona is dominated by the regular grid pattern of Ildefons Cerdà’s Barcelona Eixample, which is characterized by long streets, large square blocks with chamfered corners, and broad radial boulevards (Avinguda Diagonal and Avinguda Meridiana) connecting from center-to-edge of the city. Finally, surrounding the Eixample, are a series of regular and deformed grids of varying scale and design, which define the peripheral areas of Barcelona.
(Updated: June 30, 2017)
Urban Patterns is a series of posts from The Outlaw Urbanist presenting interesting examples of terrestrial patterns shaped by human intervention in the urban landscape over time.