“The physical planning of the new city reflects the harmony and integrated nature of its social structure. A unified planning approach assigns to each element a role in the formation of human environments.”
– The Ideal Communist City
 The Ideal Communist City by Alexei Gutnov, A. Baburov, G. Djumenton, S. Kharitonova, I. Lezava, and S. Sadovskij (Moscow University), Translated by Renee Neu Watkins, Preface by Giancarlo de Carlo
The Ideal Communist City by Alexei Gutnov, A. Baburov, G. Djumenton, S. Kharitonova, I. Lezava, and S. Sadovskij (Moscow University), Translated by Renee Neu Watkins, Preface by Giancarlo de Carlo
First written during the 1950s and translated from Italian to English in 1968, The Ideal Communist City (1968) is very much a product of its time. This does not only mean the ideological struggles of the Cold War (Capitalism vs. Communism… SPOILER ALERT! Capitalism won). It also means the symbolic height of propagating and implementing the principles of Modernist architecture and planning around the world. The principles discussed in The Ideal Communist City are merely a reformulation, repackaging and, yes, redistribution of these same ideas found in the new towns model (referred to here as the “New Unit of Settlement or NUS”) of Ebenezer Howard’s Garden Cities of To-morrow, housing models of Congrès internationaux d’architecture moderne (CIAM), and Harris and Ullman’s multi-nuclei theory in collusion with Euclidean zoning/modern transportation planning, which conveniently tells us almost any urban function can be randomly inserted almost anywhere in the city as long as ‘incompatible’ land uses are segregated.
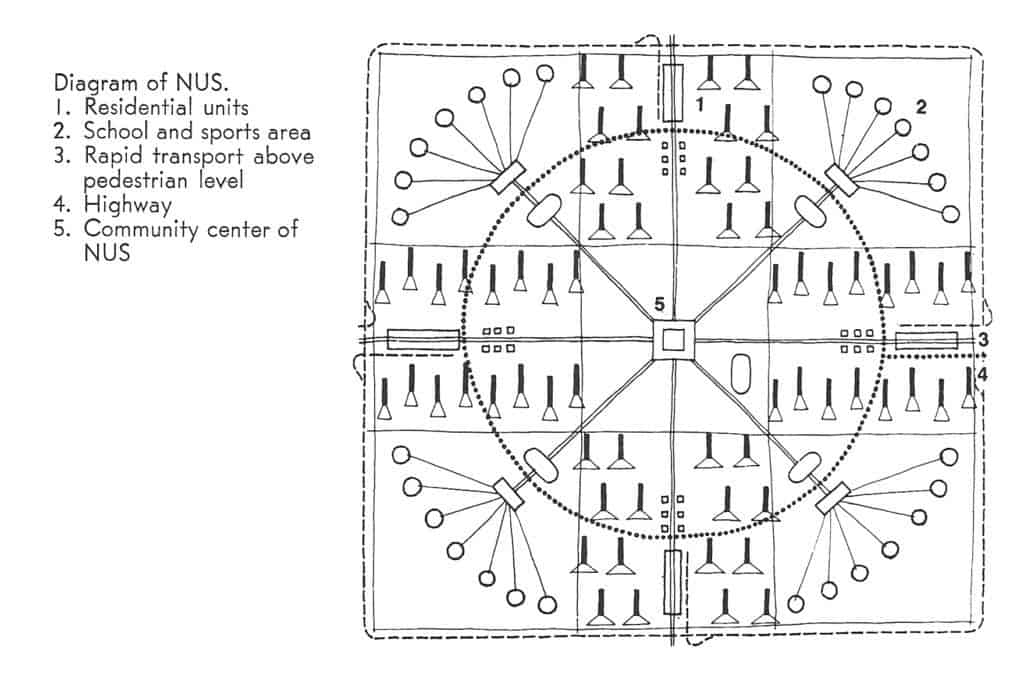 Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology
Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology
 Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.
Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.
 The Ideal Communist City by Alexei Gutnov, A. Baburov, G. Djumenton, S. Kharitonova, I. Lezava, and S. Sadovskij (Moscow University), Translated by Renee Neu Watkins, Preface by Giancarlo de Carlo
The Ideal Communist City by Alexei Gutnov, A. Baburov, G. Djumenton, S. Kharitonova, I. Lezava, and S. Sadovskij (Moscow University), Translated by Renee Neu Watkins, Preface by Giancarlo de Carlo
Hardback, 166 pages
1968, Boston: George Braziller, Inc.
You can download a PDF of the full book for free here.
From the Vault is a series from the Outlaw Urbanist in which we review art, architectural and urban design texts, with an emphasis on the obscure and forgotten, found in second-hand bookstores.


 Planning Naked | April 2016
Planning Naked | April 2016

 7. “Flipping the Strip” by Randall Arendt for the Planning Practice section (pp. 32-35) is, by far, the most important article in this month’s issue. Naturally, it is an editorial/layout nightmare as the editors of Planning Magazine almost seem to be going out of their way to undercut the content, which transforms a relatively straightforward, clear, and concise argument into a confusing presentation for the readers to follow. Mr. Arendt should be upset about how his content was butchered by the editors.
7. “Flipping the Strip” by Randall Arendt for the Planning Practice section (pp. 32-35) is, by far, the most important article in this month’s issue. Naturally, it is an editorial/layout nightmare as the editors of Planning Magazine almost seem to be going out of their way to undercut the content, which transforms a relatively straightforward, clear, and concise argument into a confusing presentation for the readers to follow. Mr. Arendt should be upset about how his content was butchered by the editors.


 About Walter Gropius
About Walter Gropius
