 Planning Naked | August & September 2016
Planning Naked | August & September 2016
by Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A, The Outlaw Urbanist contributor
Hopefully, your hilarious guide to most everything about the latest issue of APA’s Planning Magazine
The August/September issue of Planning Magazine is a Special Issue about the Local Impacts of Federal Environment Policy. It is sure to induce a headache. Hold on tight, it’s going to be a bumpy post.
Congratulations, APA Executive Director! James M. Drinan finally wrote an editorial, “Share the Street” in the From the Desk of APA’s Executive Director section (pp. 3), to hit the right notes… mostly. I did chuckle about Mr. Drinan’s comment that shared space “may appear startling at first to the average citizen.” I think what he meant was the ‘average planner.’ “The everyday experience of navigating our streets is an opportunity for planners to apply lessons – from Chicago and elsewhere – to provide leadership in shaping our evolving culture.” I never thought I would read those words in an official capacity in Planning Magazine. Amen, brother! What is that I’m feeling? Could it be … hope? Nah.
A plague o’ both your houses! “Disaster by Design in Houston?” by Ryan Holeywell (pp. 10) in the News section briefly covers the arguments (pro and con) about the role of private development in contributing to the recent spate of flooding in the Houston, Texas area. Unfortunately, the agenda-driven, black and white perspective of both sides of the issue (regulatory-driven planners vs. profit-earning developers) is the only clear thing that comes across in the article. Perhaps this is a topic requiring more room in Planning Magazine in order to more thoroughly review the issue? I came away only disgusted.
Celebrate bureaucracy, not results. “NPS, 100 Years and Counting” by Jake Blumgart (pp. 11) in the News section summarizes some of the activities celebrating the 100-year anniversary of the National Park Service (NPS) established in 1916. However, the first national park, Yellowstone, was signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant in 1872. Is the creation of a government bureaucracy really something to celebrate, I wonder?  The answer is no, which is why half of this news brief is really about money, e.g. NPS doesn’t get enough money, NPS needs more money, how can NPS get more money, etc. It is a tiresome, old school type of Planning Magazine article.
The answer is no, which is why half of this news brief is really about money, e.g. NPS doesn’t get enough money, NPS needs more money, how can NPS get more money, etc. It is a tiresome, old school type of Planning Magazine article.
Be afraid, be very afraid. In the News Briefs section (pp. 11), there’s this little tidbit of information. Home prices in seven U.S. cities climbed to record highs in April 2016 according to Standard & Poor’s/Case-Shiller’s National Home Price Index (as if S&P can be believed about anything); only 9.6 percent below the peak a decade ago. Fortunately, none of the cities listed were in Nevada or Florida. Should you be comforted or frightened? Not sure. Plan for the worse, hope for the best, I guess.
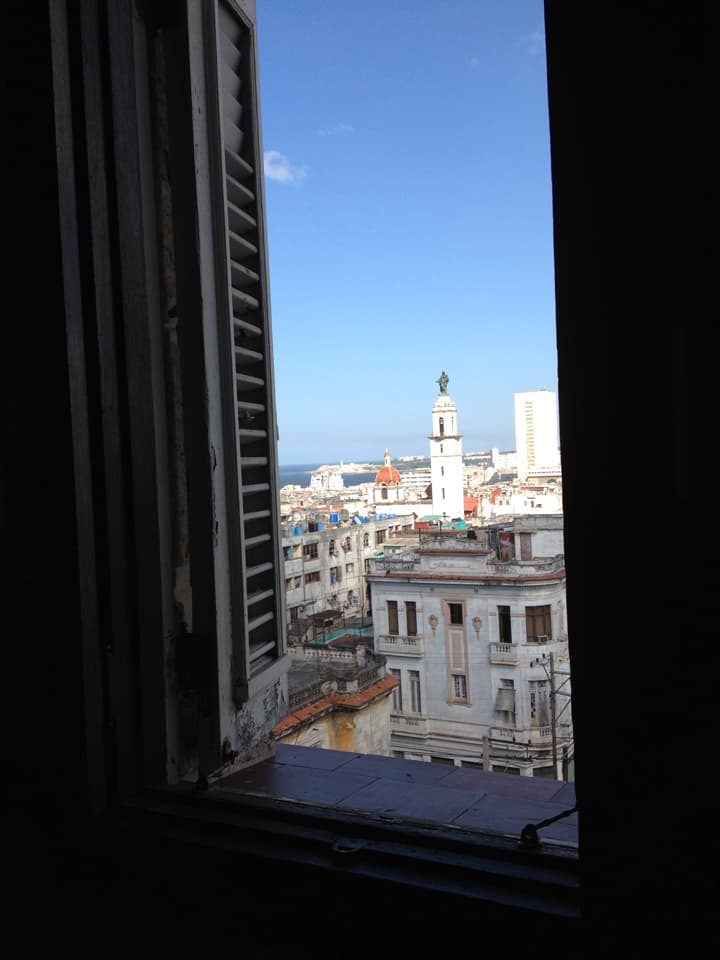
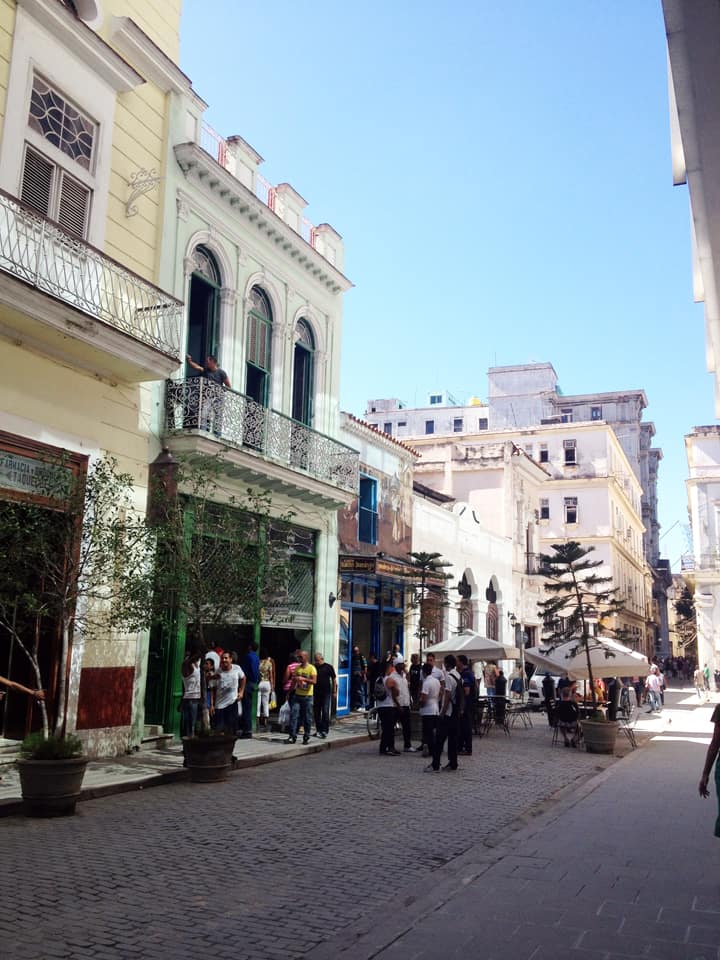
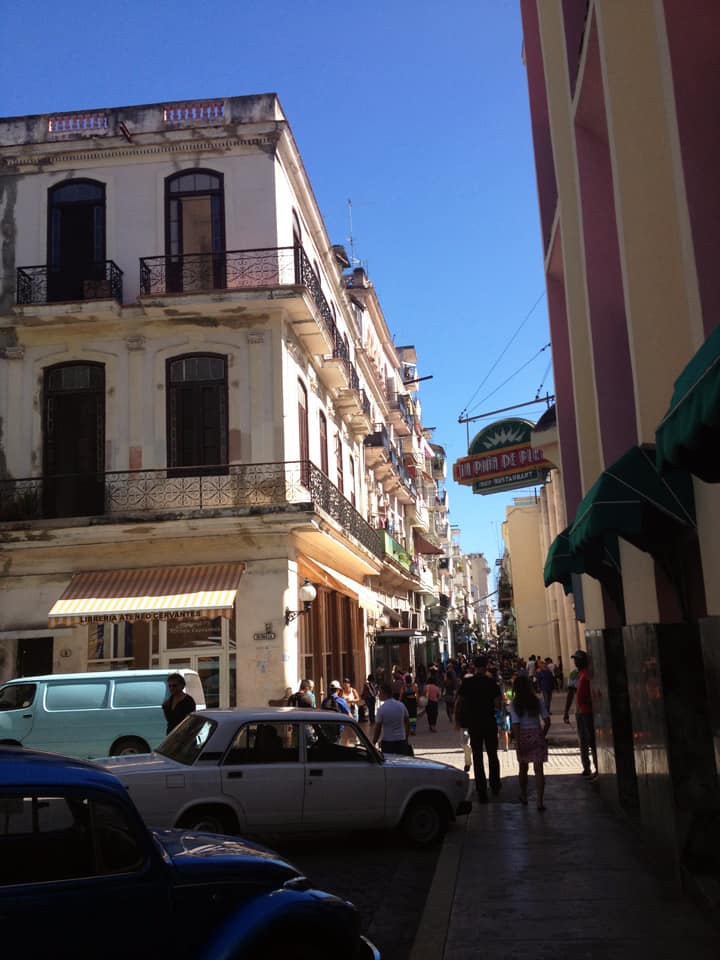
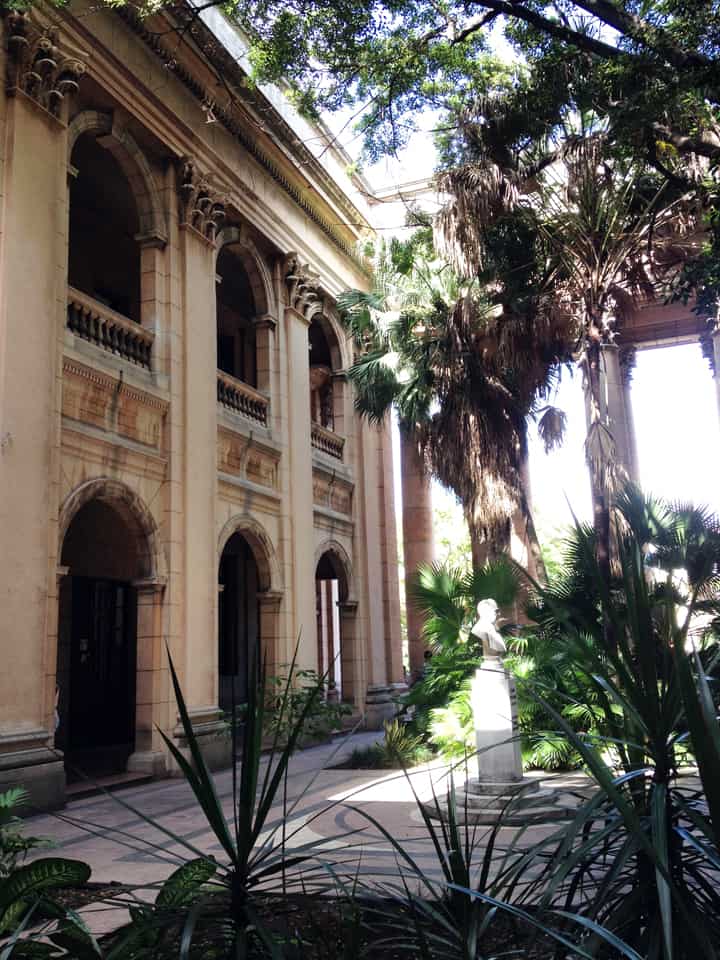
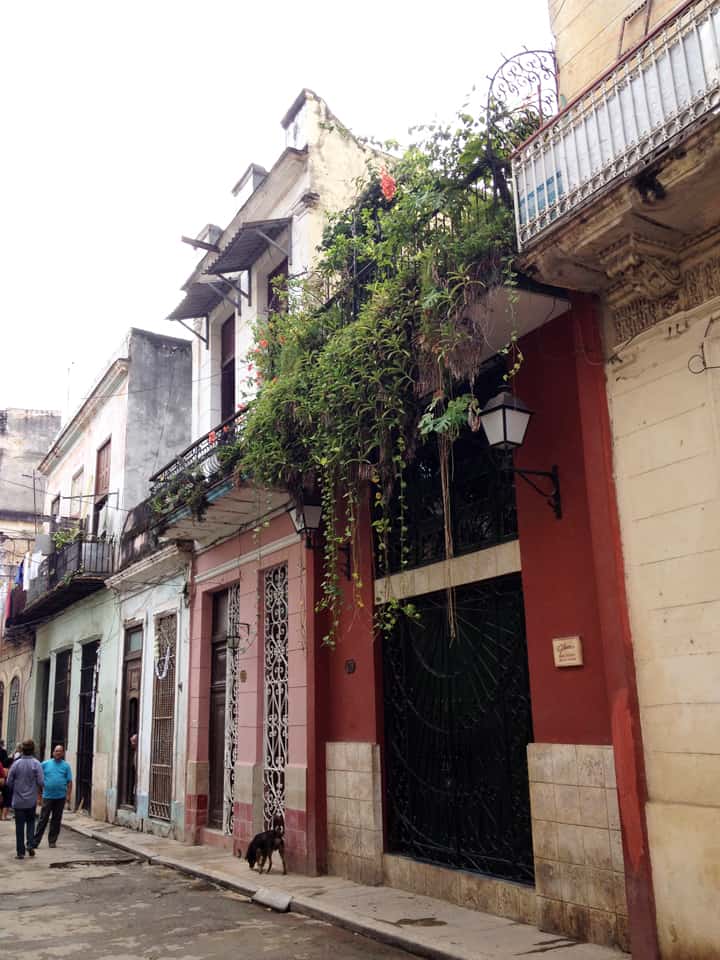
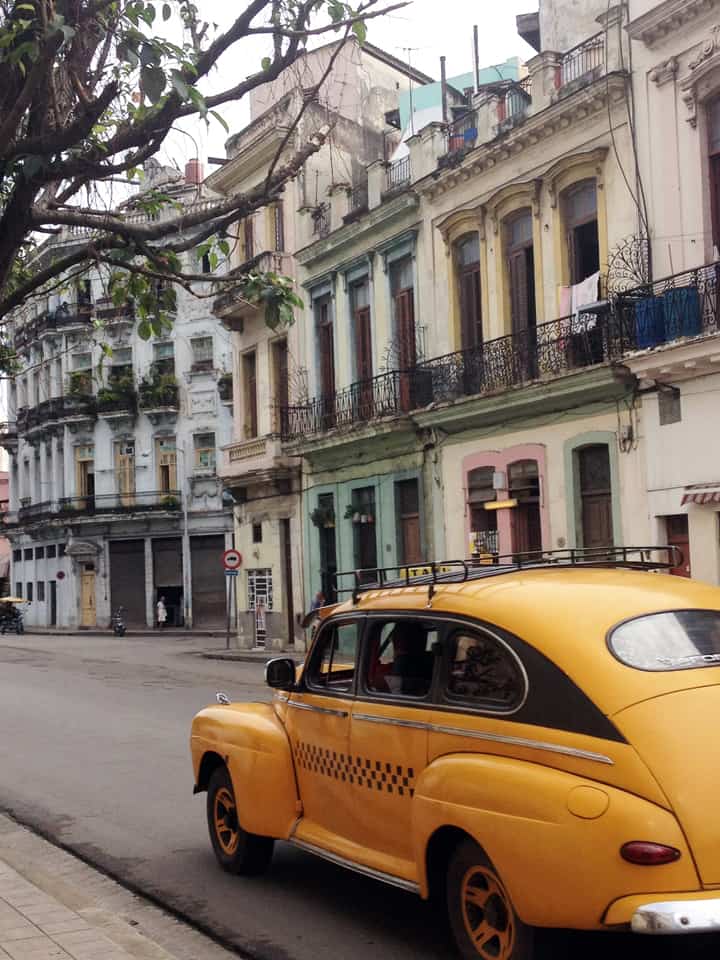
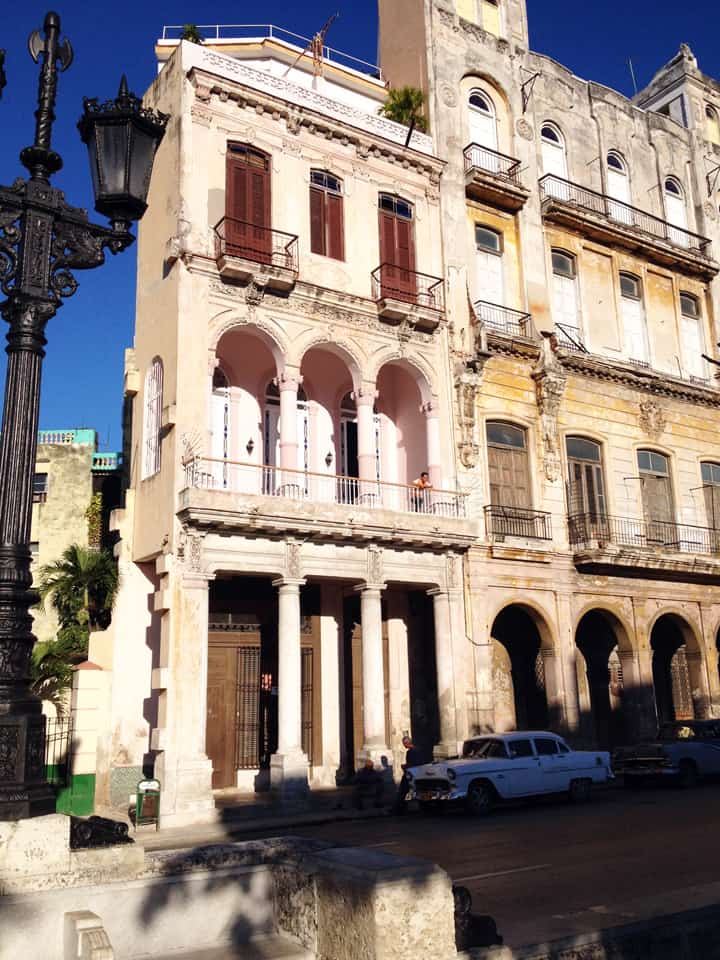
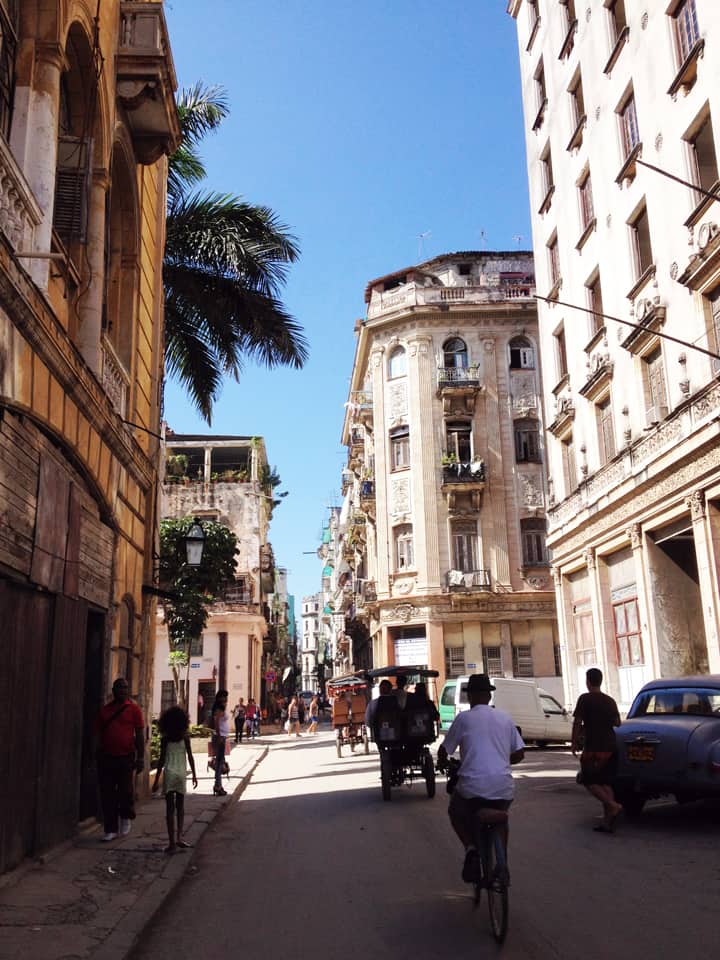
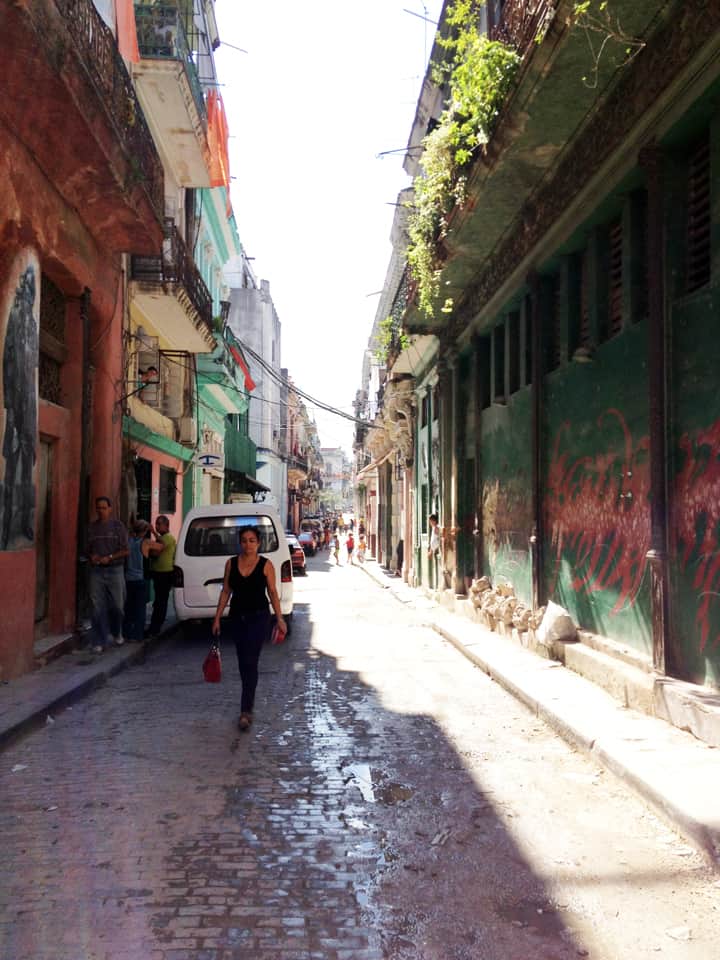
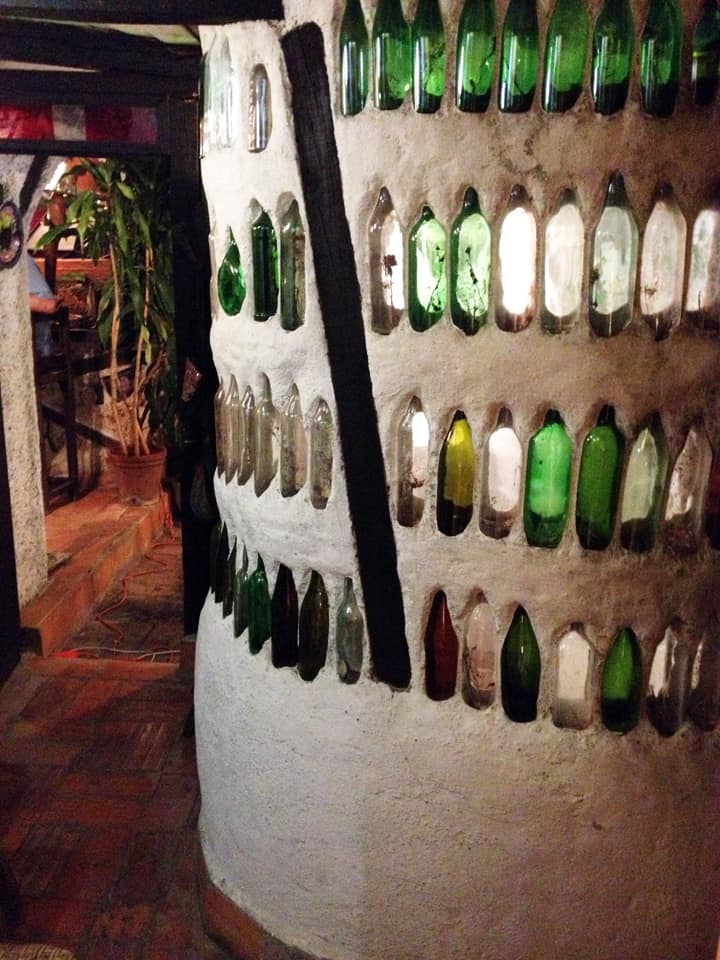
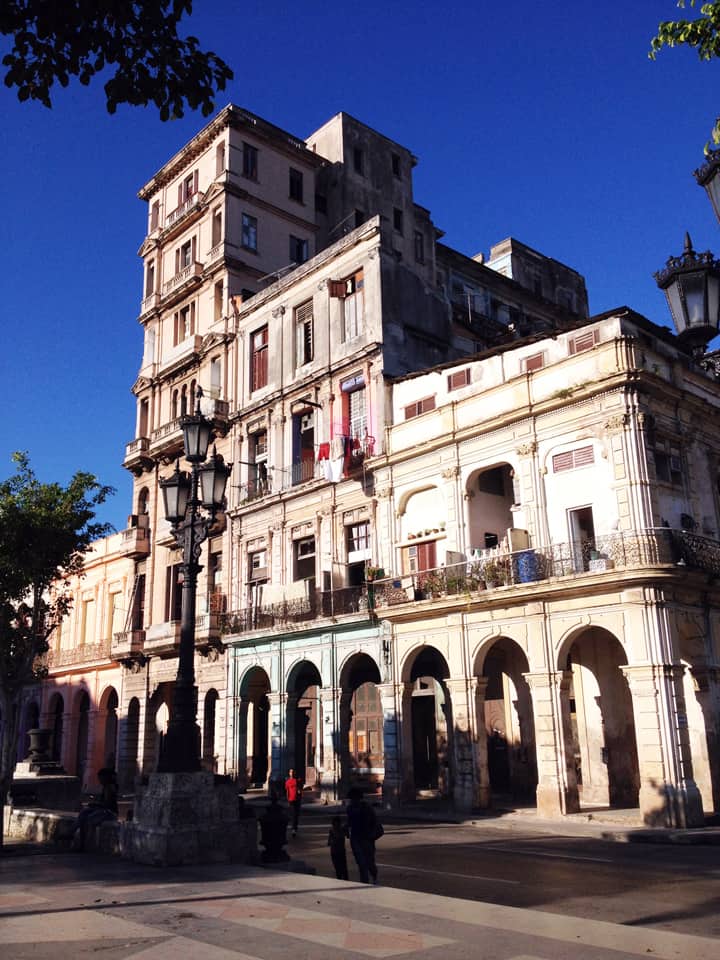
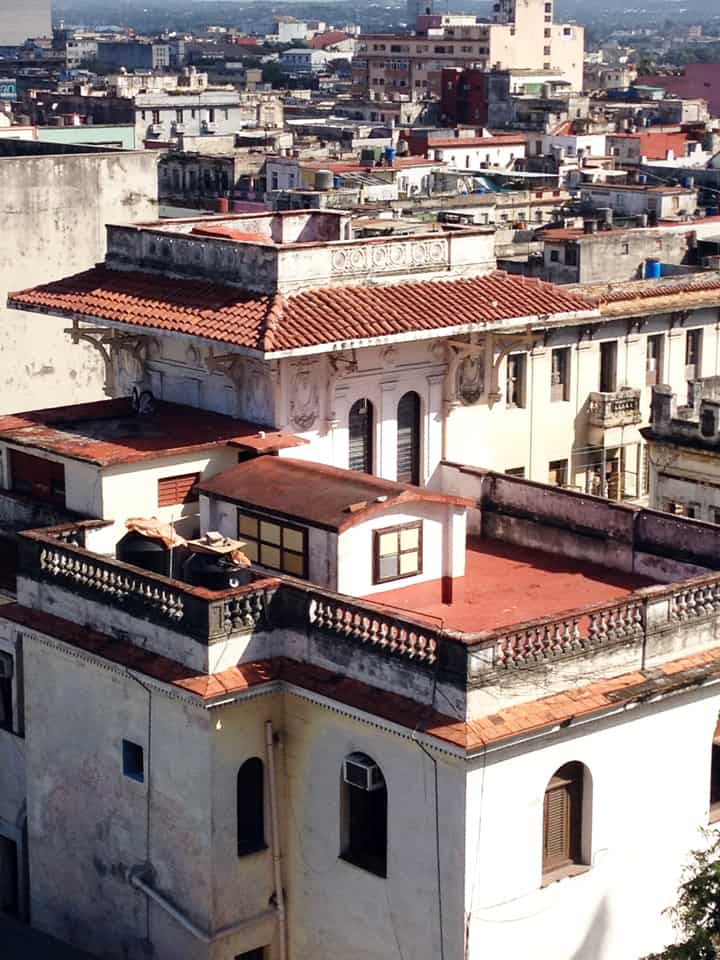
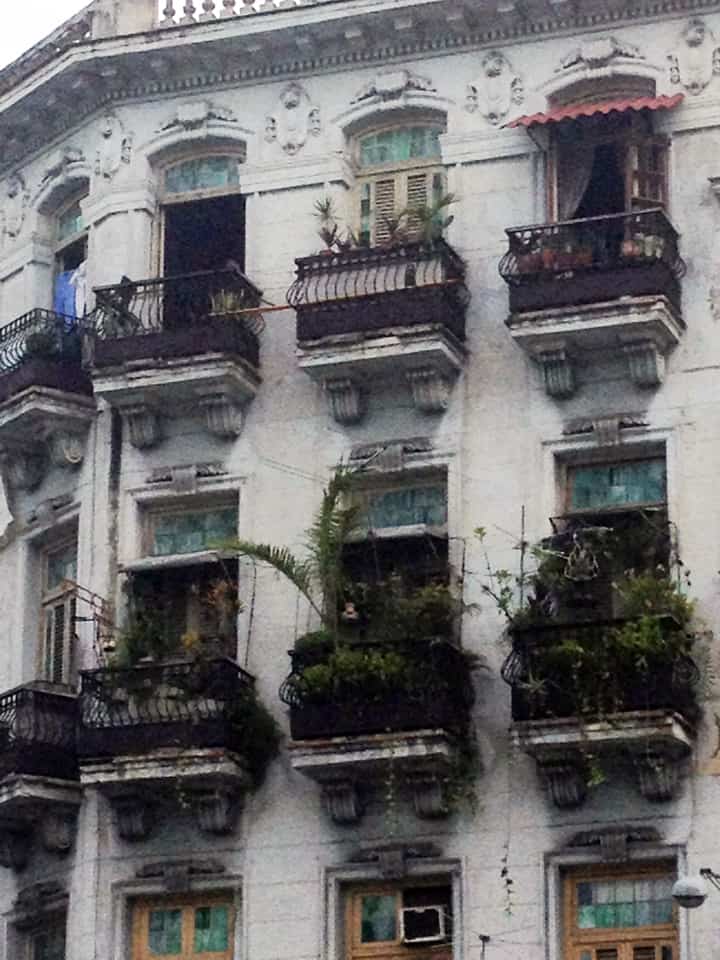
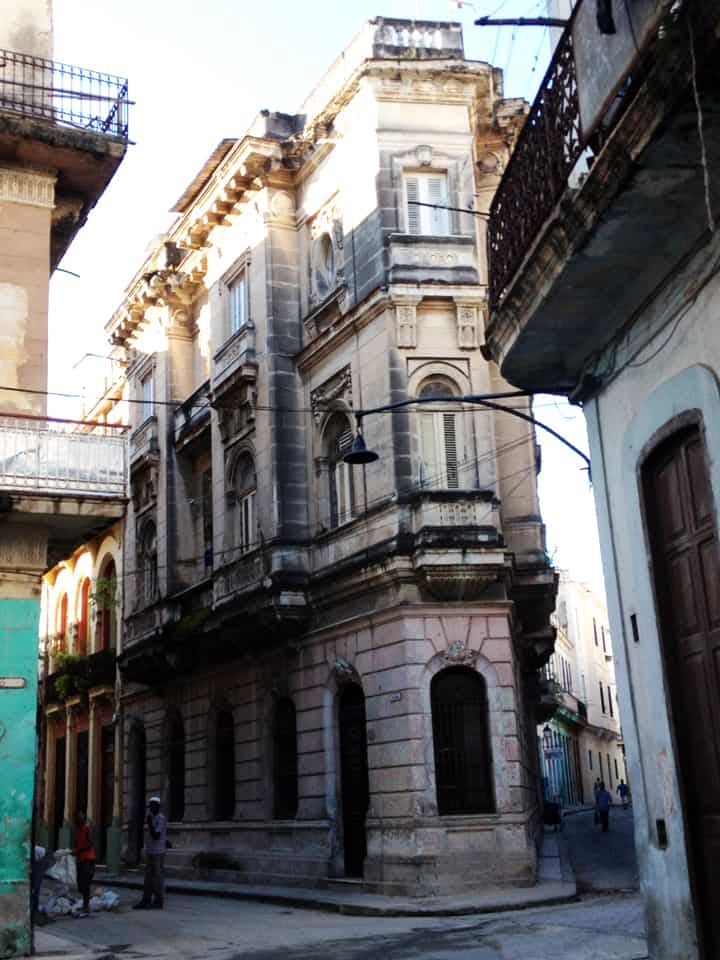
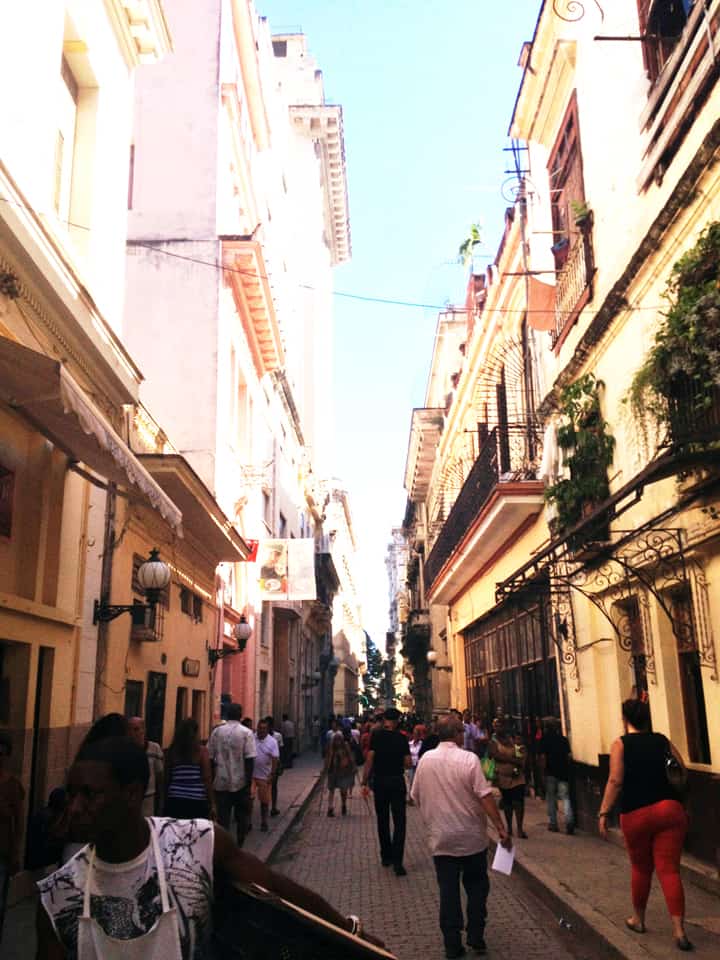
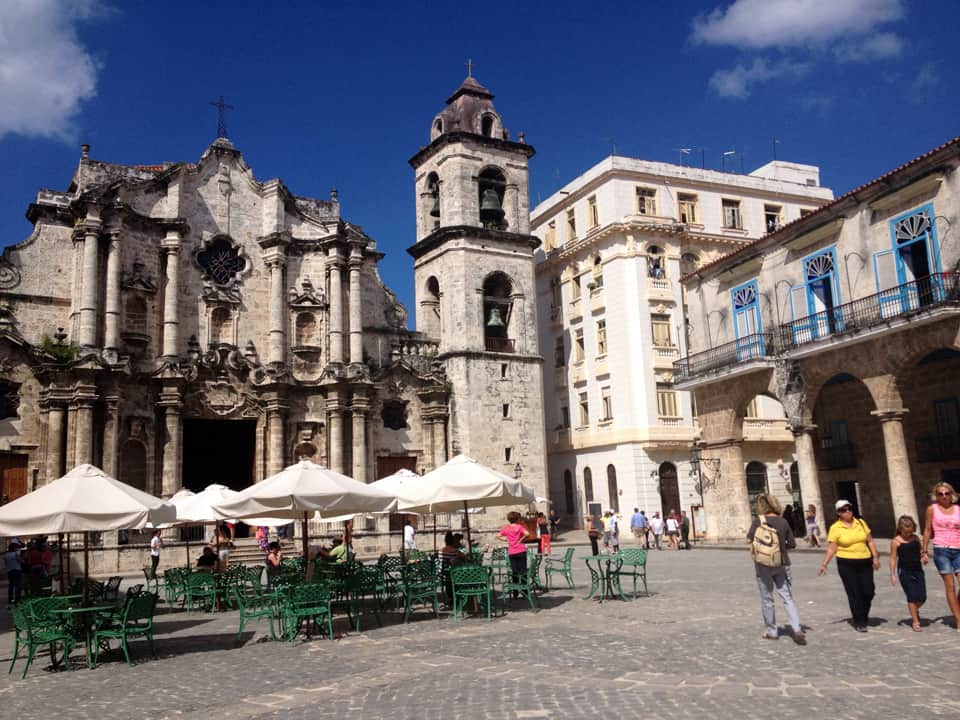
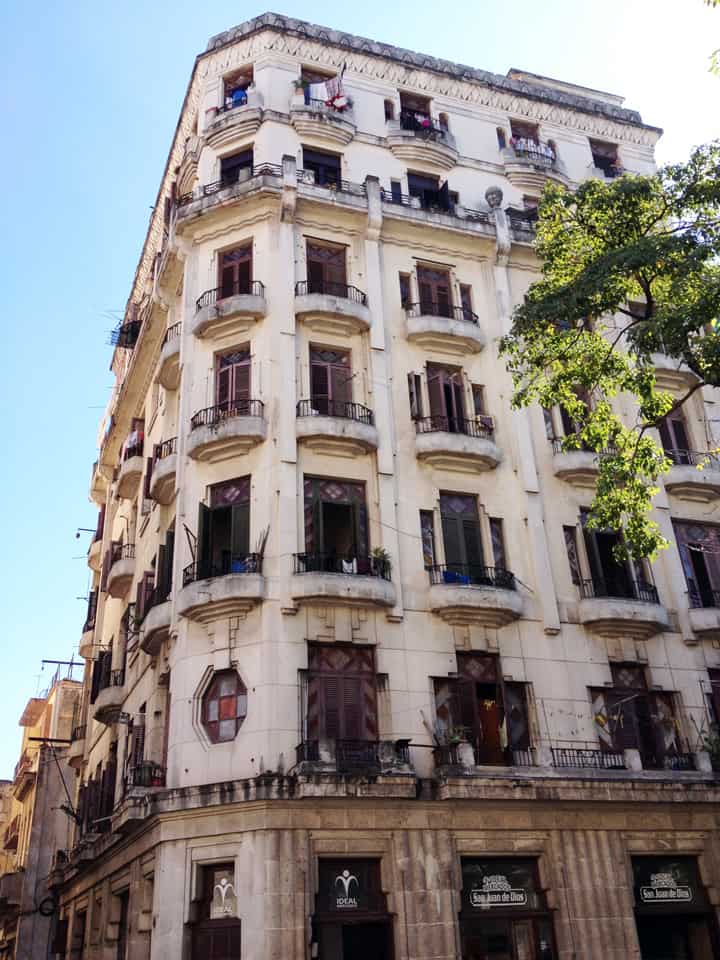
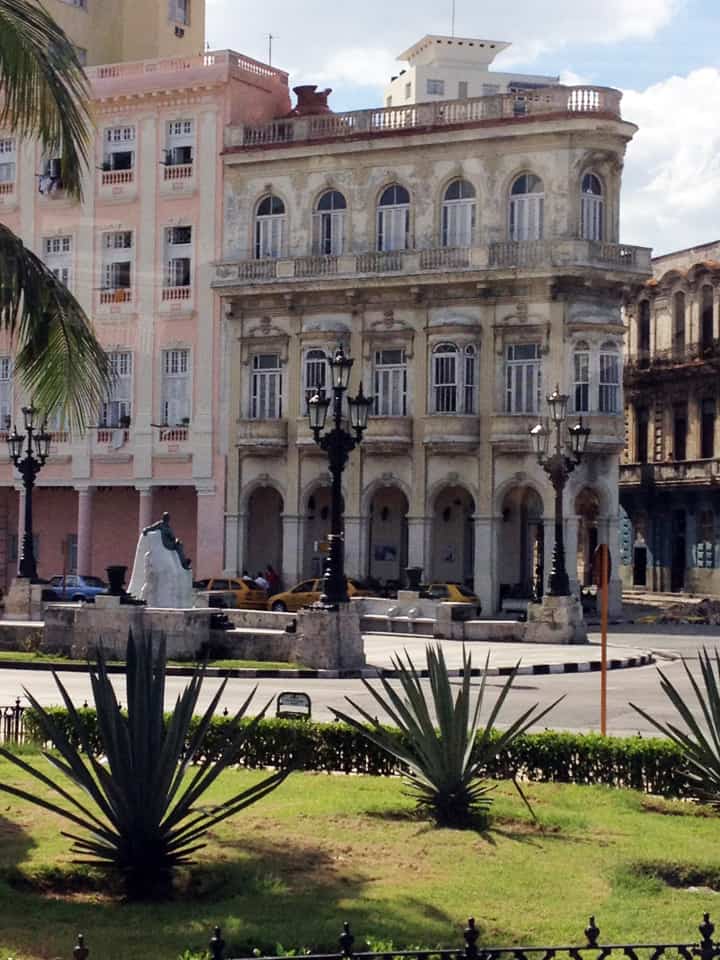
Last stand of Communism in the world. “Welcome to Cuba” by Katie Halloran (pp. 12) discusses some of the issues surrounding historical preservation and the rapid return of overseas/American tourism to Havana, Cuba. It is an interesting update but mostly lacking in specifics. There seems little doubt this is due to the opaque nature of Cuba’s communist government, which seems to be following the Chinese model of ‘opening its economy’ from 20 years ago. We hope the Cubans do not make the same mistakes as the Chinese when it comes to rapid urbanization. The differing demographic scenarios indicate Cuba has an unique opportunity to do better, given the right leadership.
Come ride my yo-yo, please. It is disconcerting when the first line of an article is blatantly false such as in “Reading Between the Lines” by Stephen D. Villavaso, JD, FAICP of the Legal Lesson section (pp. 13), which begins, “Since the 1920s, courts have regularly given clear signals to professional planners on how to plan better and, maybe more easily.” The offending words of this opening sentence are ‘clear’ and ‘better.’ The post-war disaster of American suburban sprawl and downtown decline tells a different story. It is even more disconcerting when the next sentence completely contradicts the first one so both sentences are rendered meaningless. Yeah, the author is an attorney. Having said that, Mr. Vilavaso’s review of the constitutional issues discussed in the dissent to the Baton Rouge case is enlightening. This includes Euclidean zoning restrictions of building use based on the definition of “family.” This issue sits at the crux of the problem arising because of AirBnB, i.e. unfettered expansion of land tenure rights under suburbanization (which Euclidean zoning is manifestly based and promulgated) and the property rights of homeowners to use their property at they see fit when there is little or no evidence of negative impact to neighboring properties. The final three paragraphs of this article is only a historical fluff recap (e.g. Kelo, Dolan). Ignore the nonsense at the beginning and the fluff at the end but definitely read the “Beyond the final ruling” section in the middle.
When government doesn’t work. “Before It’s Too Late” by Brian Barth (pp. 14-20) is planning masturbation at its worse. There is a well-established response to dramatic climate change in human history, which is thousands upon thousands of years old: people move. What this article makes clear is the massive amount of time, money and effort being wasted on unnecessarily studying the ‘climate refugee’ problem to death:
- Let’s do a study to see who is vulnerable;
- Let’s do a study to see where they might move;
- Let’s do a study to assess the environmental impact of a relocation;
- Let’s do a study of the flaws in the initial study;
- Let’s do a study of project costs;
- Let’s do a study about cultural loss;
- Let’s do a study about so on and so on…
All humans are ‘climate refugees.’ Otherwise, we would all be living in Africa right now (and not so many of us). Here’s the real kicker: “…the inherent challenge of navigating the dozens of local, state and federal agencies implicated in establishing a new community from scratch have kept the pace of relocation efforts at a slow slog.” This is a cause célèbre about how government is the problem, not the solution™ (1980, Ronald Reagan). The people who live in these villages will eventually solve this problem themselves because they will have no choice. Government bureaucrats and planners will continue to squeeze as much cash as they can out of the process until the solution happens on its own. The accompanying article “The Resettlement of Isle de Jean Charles” by Craig Guillot (pp. 21) about a relocation in Louisiana due to soil erosion even admits most models of relocation planning ‘have not done very well.”
When government works. “Good Habitats Pay Off” by Madeline Bolin (pp. 22-27) is a stark contrast to the previous article. Bolin’s article actually discusses alternative tools to full implementation of the Endangered Species Act (ESA) such as habitat mapping, Habitat Conservation Plans (HCP) and variations thereof. There is not a single mention about money. In fact, Bolin’s article effectively demonstrates how local, state and federal government can effectively work together with the private sector to implement environmental protection measures. It is informative, interesting and useful. The insert “Federal Environment Laws and Land Use” by Ms. Bolin (pp. 26) is a brief, useful checklist of relevant legislation.
I feel like I’m taking crazy pills. “The ‘If’ Game” by Allen Best (pp. 28-35) is when I lost my patience with this special issue of Planning Magazine, began to stop diligently reading and went into browse mode. However, the real kicker is in the next article “Is Nuclear Clean Power?” by Susannah Nesmith (pp. 36-39). Here is a short summary: 1) nuclear power is bad for habitats; 2) a potential problem disrupting local habitat is identified with an intake pipe at a nuclear power plant; 3) a solution is identified (e.g. installing a grate); 4) it takes the Federal government 8 YEARS to approve the grate installation: 5) ergo the problem with nuclear power is it destroys habitats. Does anyone else not notice the Federal bureaucracy prevented the installation of a solution for years that, at worst, would take a few weeks to implement, therefore the problem is not nuclear power but the Federal government?!?!
Save yourselves! It’s too late for me! Sorry readers, my sanity couldn’t take any more of the drivel in this special issue about the Local Impacts of Federal Environment Policy in Planning Magazine.
Planning Naked is an article with observations and comments about a recent issue of Planning: The Magazine of the American Planning Association.


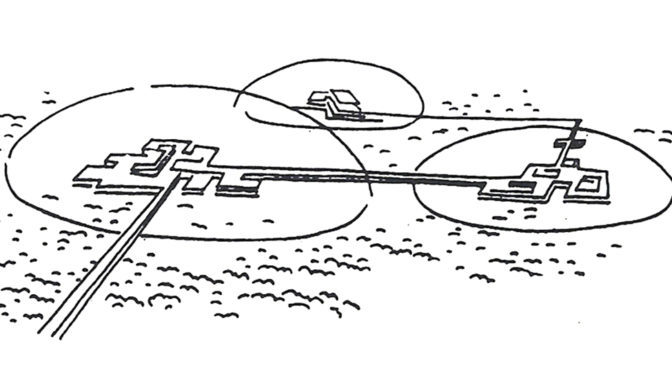

 Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology
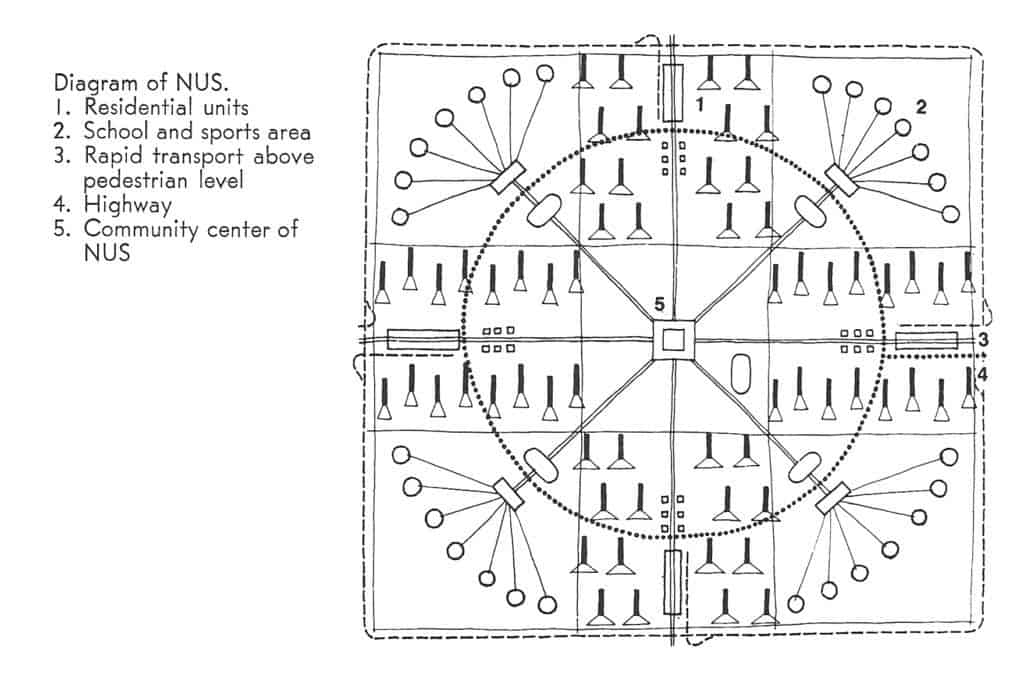
Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.
Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.




















