 Planning Naked | March 2017
Planning Naked | March 2017
by Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A, The Outlaw Urbanist contributor
Your (hopefully hilarious… but not so much this month) guide to most everything about the latest issue of APA’s Planning Magazine
NOTE: The United States of America inaugurated Donald J. Trump as its 45th President on January 20, 2017, and, in response, Planning Magazine turns the crazy up to eleven.
Making Joseph Goebbels Proud. “Placemaking as Storytelling” by James M. Drinan, JD (From the Desk of APA’s Chief Executive Officer, pp. 3) contains some disturbing language. Drinan points out, “Research shows that coupling stories with data produces a significant increase in the retention rate of that data.” Basically, he is correct. However, it is important to clarify Drinan is not precise. FYI: Never expect precision from a lawyer because you will always be disappointed. It is more accurate to say that using data to better tell a story about an objective truth is an excellent means of increasing retention about both that story, the data, and the truth. It reinforces the objectiveness of both observer and the observed. Using data loosely to reinforce a lie is propaganda. This is a nuanced but important distinction. This is because Drinan goes on to state, “it is crucial to control (our emphasis) the narrative-the story.” This is a defensible position for a propagandist but not a scientist. Drinan (perhaps unintentionally) reveals he is discussing politics and propaganda, not scientific truth when you consider what he manifestly fails to say in a subsequent sentence. The key is the citation of planners as storytellers, authors, illustrators, and editors. What is missing? The answer is scientists. This ‘frontpage editorial’ is one of the most disturbing things I have read in Planning Magazine in years because it advocates for the very thing it pretends to be against. This is the insidious nature of the status quo reasserting itself against change. Forewarned is forearmed. NOTE: Having now read this, I am angry with myself for leaving this March 2017 issue of Planning Magazine sitting unread on my desk for two months. The previous months’ issues lulled me into a false sense of security. My mistake…
OMG! And I am only on page eight. “Federal Tax Credit Uncertainty Puts Affordable Housing at Risk” (News Section, pp. 8-9) by Dean Mosiman – a Madison city government reporter for the Wisconsin State Journal. RED FLAG, RED FLAG: Scott Walker is evil incarnate – contains some really bad reporting as Planning Magazine embarks on Drinan’s explicit promise to attempt to ‘control’ the story. First, it assumes a reality that is non-existent. “For 30 years, federal affordable housing tax credits have been the nation’s most potent tool to create housing for the homeless and low-income households.” Really? Have you been to Los Angeles lately? This bastion city in a bastion state of the Democratic Party has one of the worst, most despicable, and most shameful homeless problems I have ever seen in the Western world over the last three decades. It makes me sick to my stomach just thinking about what I saw and smelled in L.A. Everyday, there is another article in the mass media about an overwhelming lack of affordable housing in cities around the world including the USA. The tax credit is not a potent tool but a failed one. According to the article, the tax credit “had a major impact on the nation’s housing stock, helping create 2.8 million affordable units nationwide.” The use of ‘major’ here is shameless hyperbole and the ‘helping create’ means there might be an indirect benefit but not direct causation. Of course, these 2.8 million units were most likely woefully insufficient to replace the smaller (in square footage), more affordable historic housing stock demolished by public and private agencies during the same period. This news article is about one thing: fear that the pigs might not be able to eat at the government trough in the near future. Then, at the end of the article, the author implicitly concedes this is fear-mongering by stating the tax credit “is likely to survive.” Nothing to see here, folks, move on home! This is ‘fake news.’
People Matter. Planning Magazine ‘buries the lead’ with the “Miami Street Experiment Prioritizes People” by Susan Nesmith (News Section, pp. 9-10) by discombobulating the story across two pages, which is bad editing and bad graphic design. It makes you wonder what APA has against putting “people over cars” and “slowing traffic (with) no big gridlock.” The experiment is over but the “fancy crosswalks” remain: really, fancy crosswalks? Fancy? It is a good thing I have plenty of hair to pull out. This experiment and the subsequent attempts for a more humanistic redesign of this Miami boulevard is something that Planning Magazine needs to herald and promote, not deride as some quaint idea. Is this a failure of Ms. Nesmith’s writing or the editors of Planning Magazine? Perhaps both. I am not sure.
In ‘Do No Harm’ News. “Remaking Vacant Lots to Cut Crime” by Martha T. Moore (News Section, pp. 10) is an interesting story about a low-cost, temporary solution for vacant properties in urban conditions; as long as people and agencies understand it is not a long-term solution. All in all, however, I like the concept.
Beware of Florida Lawyers Bearing Gifts. This months’ Legal Lessons section (“Staff Reports: A Lawyer’s Take by Mark P. Barnebey, pp. 11) is one of those standard-type of articles Planning Magazine re-runs every 3-5 years due to new, young professionals entering the workforce. I remember reading the last two iterations of this article about staff reports (respond the young people, “He must be really old”). Barnebey’s article is fine for this purpose though he undersells just how influential of a role the staff report can play in quasi-judicial decisions by elected officials, if carefully constructed.
 Strike that. Reverse It. Welcome, Florida Lawyers Bearing Gifts. However, having said that, the more advanced state of staff reports in Florida – due to their quasi-judicial nature associated with the 1985 Growth Management Act and subsequently, Mr. Barnebey’s greater experience with the best of such staff reports – starkly contrasts with the next article, “The Better STAFF REPORT” by Bonnie J. Johnson (pp. 20-24). Allow me to state more simply the point that I believe Dr. Johnson is attempting to convey: the best staff reports combine: 1) well-written content with 2) well-designed visuals and 3) promptly get to the point. Like most planners, Dr. Johnson’s article manages to fail on all these counts. Johnson does not even seem to know her audience for this article (i.e. there are lots of different types of planners and staff reports) so she makes the mistake of trying to address ALL possible audiences. The result is inadequate for everyone. The graphic design of this article makes the content even more confusing. I mean it is really, really bad but hardly surprising. In my experience, most planners are woefully under-trained in the art of graphic design. I do not know if this is the fault of Dr. Johnson or Planning Magazine but, seriously, reading this article gave me a fucking headache.
Strike that. Reverse It. Welcome, Florida Lawyers Bearing Gifts. However, having said that, the more advanced state of staff reports in Florida – due to their quasi-judicial nature associated with the 1985 Growth Management Act and subsequently, Mr. Barnebey’s greater experience with the best of such staff reports – starkly contrasts with the next article, “The Better STAFF REPORT” by Bonnie J. Johnson (pp. 20-24). Allow me to state more simply the point that I believe Dr. Johnson is attempting to convey: the best staff reports combine: 1) well-written content with 2) well-designed visuals and 3) promptly get to the point. Like most planners, Dr. Johnson’s article manages to fail on all these counts. Johnson does not even seem to know her audience for this article (i.e. there are lots of different types of planners and staff reports) so she makes the mistake of trying to address ALL possible audiences. The result is inadequate for everyone. The graphic design of this article makes the content even more confusing. I mean it is really, really bad but hardly surprising. In my experience, most planners are woefully under-trained in the art of graphic design. I do not know if this is the fault of Dr. Johnson or Planning Magazine but, seriously, reading this article gave me a fucking headache.
Meanwhile. “Here comes the Sun” by Charles W. Thurston (pp. 25-29) is the type of article you get from professional organizations nearly four decades after a nation abandons nuclear power.

The Blood Boils Over. But what really gets the blood boiling is Planning Magazine: 1) makes the preceding article the subject of this month’s cover (see above) instead of this article ‘buried’ at the end of the feature articles, “Life and Death Every Quarter Hour” by Jeffrey Brubaker (pp. 30-33); and, 2) seems blissfully unaware of the contrasting traffic fatalities data in this article (35,092 death in 2015) compared to the article about wildlife crossings, i.e. 200 fatalities associated with collisions with wildlife. That is right. This month’s Planning Magazine dedicates twice as many pages to an issue involving 6/1000th the number of traffic deaths. Worst still, the subtitle of this article claims “mixed results” for what is a complete failure. Finally, at the end, Planning Magazine adds a “The opinions expressed in the article are his own” (meaning Mr. Brubaker) disclaimer. God forbid that anyone might think APA and Planning Magazine are anti-automobile. And the thing is, Mr. Brubaker’s article is mild. It does not go nearly far enough in pointing the profession’s hypocrisy on this issue. Here is the gist: in 60 years, nothing has changed. There is still a death caused by vehicular traffic every quarter hour in the United States.
That is it. I cannot take any more of this month’s issue. I may have to stop reading Planning Magazine in the best interests of my health because you would not believe the migraine headache I have right now. Shame on you, Planning Magazine. The best article this month was written by a Florida attorney.
Planning Naked is an article with observations and comments about a recent issue of Planning: The Magazine of the American Planning Association.








 Planning Naked | March 2017
Planning Naked | March 2017 Strike that. Reverse It. Welcome, Florida Lawyers Bearing Gifts. However, having said that, the more advanced state of staff reports in Florida – due to their quasi-judicial nature associated with the 1985 Growth Management Act and subsequently, Mr. Barnebey’s greater experience with the best of such staff reports – starkly contrasts with the next article, “The Better STAFF REPORT” by Bonnie J. Johnson (pp. 20-24). Allow me to state more simply the point that I believe Dr. Johnson is attempting to convey: the best staff reports combine: 1) well-written content with 2) well-designed visuals and 3) promptly get to the point. Like most planners, Dr. Johnson’s article manages to fail on all these counts. Johnson does not even seem to know her audience for this article (i.e. there are lots of different types of planners and staff reports) so she makes the mistake of trying to address ALL possible audiences. The result is inadequate for everyone. The graphic design of this article makes the content even more confusing. I mean it is really, really bad but hardly surprising. In my experience, most planners are woefully under-trained in the art of graphic design. I do not know if this is the fault of Dr. Johnson or Planning Magazine but, seriously, reading this article gave me a fucking headache.
Strike that. Reverse It. Welcome, Florida Lawyers Bearing Gifts. However, having said that, the more advanced state of staff reports in Florida – due to their quasi-judicial nature associated with the 1985 Growth Management Act and subsequently, Mr. Barnebey’s greater experience with the best of such staff reports – starkly contrasts with the next article, “The Better STAFF REPORT” by Bonnie J. Johnson (pp. 20-24). Allow me to state more simply the point that I believe Dr. Johnson is attempting to convey: the best staff reports combine: 1) well-written content with 2) well-designed visuals and 3) promptly get to the point. Like most planners, Dr. Johnson’s article manages to fail on all these counts. Johnson does not even seem to know her audience for this article (i.e. there are lots of different types of planners and staff reports) so she makes the mistake of trying to address ALL possible audiences. The result is inadequate for everyone. The graphic design of this article makes the content even more confusing. I mean it is really, really bad but hardly surprising. In my experience, most planners are woefully under-trained in the art of graphic design. I do not know if this is the fault of Dr. Johnson or Planning Magazine but, seriously, reading this article gave me a fucking headache.
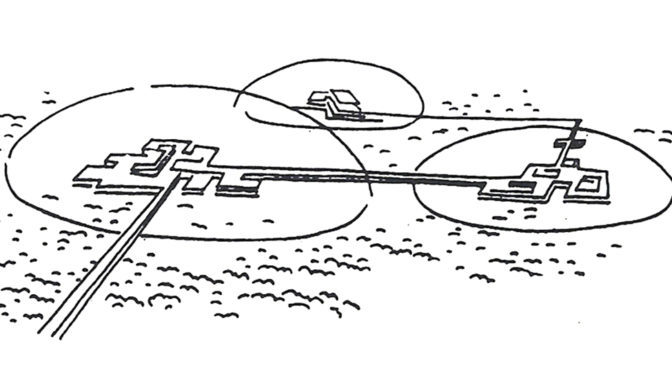

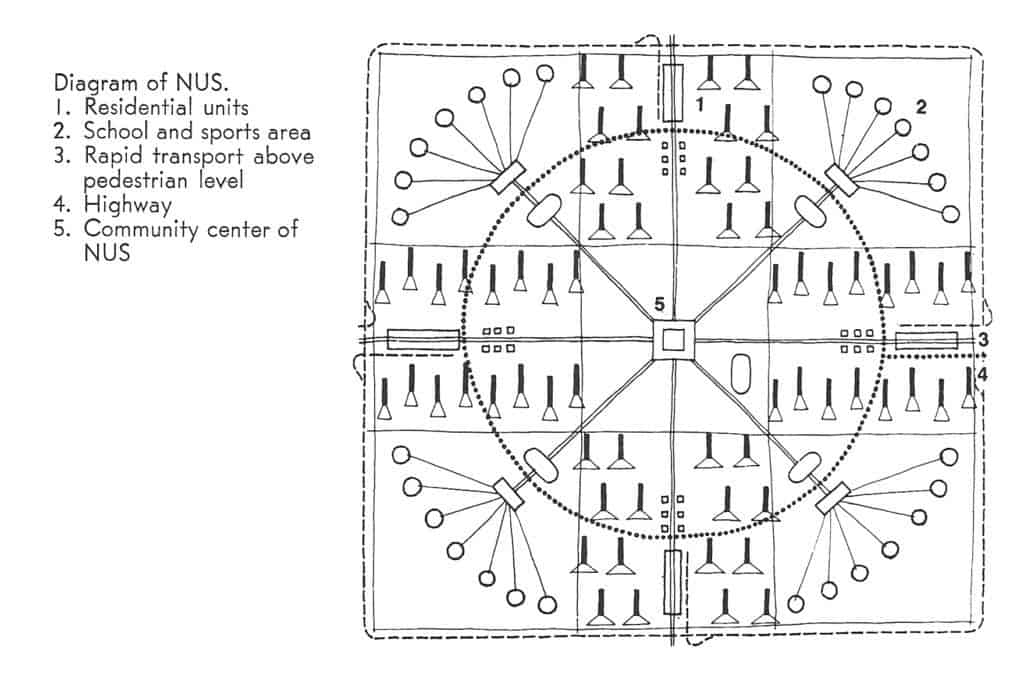 Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology
Of course, the key difference is the authors’ explicitly state the failure of these ideas to “reach their full potential” in Western societies is due to the corrupting influence of capitalism as a political and economic system. This is a conceit that has been badly exposed with time. If anything, capitalism more ruthlessly exploited the economic potentials of Modern ideas by taking them to their logical and, ultimately, extreme conclusion; probably more so than even most devoted CIAM architect ever imagined. The real danger about The Ideal Communist City is that younger readers (Millennials and generations thereafter) without any first-hand experience of the Cold War might make the mistake of thinking they are reading something original and entirely different because it’s wearing Soviet-era clothing. However, it is the same, tired planning paradigm we have been hearing about and (unfortunately) living with over the last 80+ years. To be fair, another key difference in this book is the desire of Soviet-era planners to adopt a model that segregates land uses from one another while still actively promoting manufacturing, mass production, and industrialization. Younger readers might also think this represents a somewhat unique perspective from the point of view of architecture and planning. However, it is really only evidence of Soviet preoccupation – even obsession – with Western societies’ manufacturing prowess at the time. In this sense, Soviet failure to compete with the success of Western capitalistic societies contradicted the ‘means of production’ arguments underpinning Karl Marx and Frederick Engel’s The Communist Manifesto and Marx’s Das Capital; that is, direct evidence that communism was a flawed political and economic system based on totalitarianism masquerading as a false ideology Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.
Having said all that, The Ideal Communist City is an important historical document that anyone interested in town planning should probably be exposed at some point, as long as the book is placed within its proper context for readers, especially post-Cold War ones. There are, in fact, relatively few flights of fancy in this book; the most amusing one being the common idea in science fiction that cities will eventually be covered by climate-controlled plastic domes (see Featured Image of this post at the top). The authors’ statistical projections of urban populations are way off, hilariously so. Early in the book, the authors project that 75% of the world’s population will live in urban areas by the year 2000 when it fact we only passed the 50% threshold in the last decade (due to the corrupting influence of capitalism, no doubt). The model of the NUS stretches believability despite the authors’ best – though somewhat halfhearted – efforts to address accommodating population growth during the transition period between one NUS being occupied and the next one being constructed. This is because these Soviet-era planners ultimately have a static view of the city. In hindsight, one might fairly argue the communist NUS model has already been better implemented and realized in cities such as Milton Keynes in England, the Pilot Plan of Brasilia in Brazil, or perhaps even some areas of America Suburbia, despite the problematic nature of such places as extensively discussed elsewhere in the literature. In the end, the Ideal Communist City is perhaps best at asking some interesting questions about cities but the answers provided are all too familiar and depressing to seriously contemplate. As Christopher Alexander famously said, “a city is not a tree.” It seems the same is as true for communist cities as it ever was for capitalistic ones. In the end, human nature is always more pervasive than any political ideology.