The Architecture and Film Course Series reviews the seductive correspondence between cinema and architecture. Of all the fine arts, cinema and architecture seem to uniquely correspond due to their natures as both an art and a science. In no small part, this is because both deploy many of the same concepts in a superficial and/or substantive way, i.e. representation, presentation, functionality, and materiality. Over the last four decades, startling technological advances, mostly deriving from computer science, have further blurred the distinction between cinema and architecture. Collectively, this tends to obscure the most important aspect, which is architecture’s impact on the dual aims of cinema, e.g. narrative and technology. Part I, “Do Architects Dream of Celluloid Buildings” reviews the conceptual, historical and technological correspondence between cinema and architecture. Part II, “The Architectural Competence in Cinema” and Part III, “The Best of Both Worlds”, review the cinematic use of architectural precedents and typologies in crafting distinctive film-grammars in support of narrative and characterization.  The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (6.0 course). Click here to purchase this full course series ($39.99).
The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (6.0 course). Click here to purchase this full course series ($39.99).
Key concepts: abnormal scale, analogy, architectural typologies, cinema, cultural appropriation, extended narratives, fantasy, historical juxtaposition, historical intensification, historical precedent, hyperreality, language, narrative, representation, scale, science fiction, and technology.
Includes a three(3) two-hour video presentations and PDFs of the supplementary materials and slide handouts for each course.
Part 1 Film and Television Topics
The Wizard of Oz, A Trip to the Moon, Game of Thrones, Star Wars, The Hunger Games, Friends, New Girl, Planet of the Apes, Alice in Wonderland, Star Trek, To Kill a Mockingbird, Back to the Future, Westworld, When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth, Jurassic Park, The Wedding Singer, The Terminator, Babylon 5, Captain America, Avatar, Battlestar Galactica, It’s a Wonderful Life, Zelig, Forrest Gump, Jupiter Rising, Toy Story, Tron, Resident Evil, Total Recall, The Matrix, A Scanner Darkly, Contagion, American Psycho, Metropolis, Blade Runner
Part 2 Film and Television Topics
Alien, War of the Worlds, V for Vendetta, Blade Runner, Jaws, Watchmen, Batman, The Rape of Doctor Willis, Superman, The Lady in the Water, Close Encounters of the Third Kind, Star Wars, The Godfather, Game of Thrones, The Lord of the Rings, Baywatch, The Shawshank Redemption, Thor, From Hell, The Lodger, James Bond, Chinatown, Logan’s Run, Four Weddings and a Funeral, Stargate, Battlestar Galactica, Cube, 1984, Divergent, The Truman Show, Pleasantville, Metropolis, V, Independence Day, Invasion of the Body Snatchers
Part 3 Film and Television Topics
Star Trek, Harry Potter, Blade Runner, The Lord of the Rings, Citizen Kane, Batman, Doctor Who, Inception, A Nightmare on Elm Street, Spellbound, Doctor Strange, 2001: A Space Odyssey, Interstellar, Star Wars, Logan’s Run, Alien, Dune, Battlestar Galactica, Zoolander, The Martian Chronicles, Invasion of the Body Snatchers, District 9
Please note there may be a delay for a couple of hours before you are able to access the course because we have to confirm receipt of payment for each order before completing the purchase.
About the Instructor
 Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A is an architect and planner with extensive experience in urban planning and design, business management and real estate development, and academia. He is a Professor of Urban Design at the Savannah College of Art and Design. Mark has been a visiting lecturer at the University of Florida, Georgia Tech, Architectural Association in London, the University of São Paulo in Brazil, and Politecnico di Milano in Italy.
Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A is an architect and planner with extensive experience in urban planning and design, business management and real estate development, and academia. He is a Professor of Urban Design at the Savannah College of Art and Design. Mark has been a visiting lecturer at the University of Florida, Georgia Tech, Architectural Association in London, the University of São Paulo in Brazil, and Politecnico di Milano in Italy.
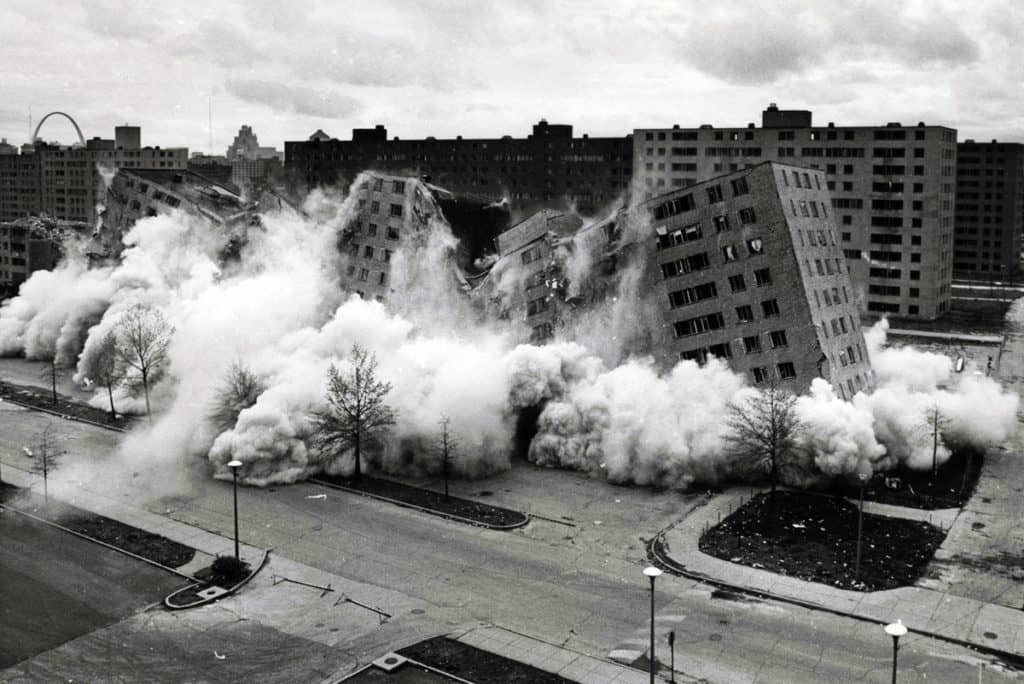
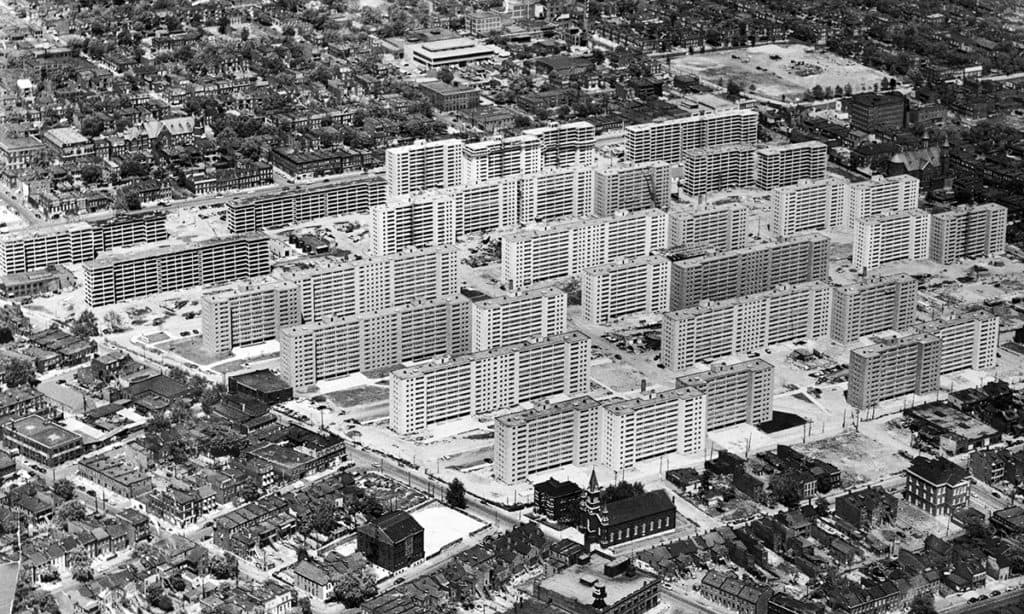
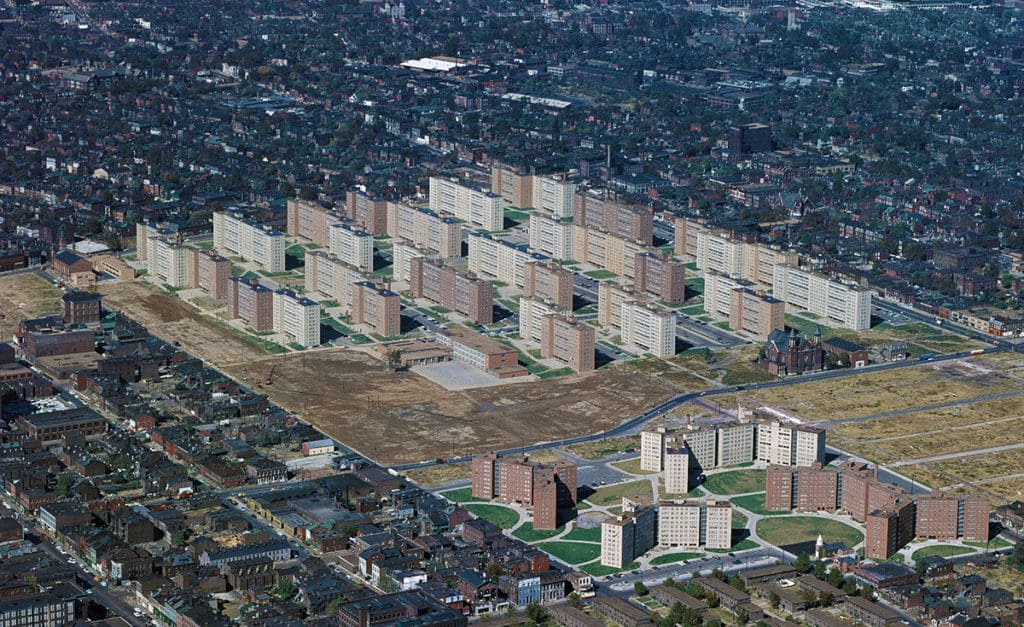
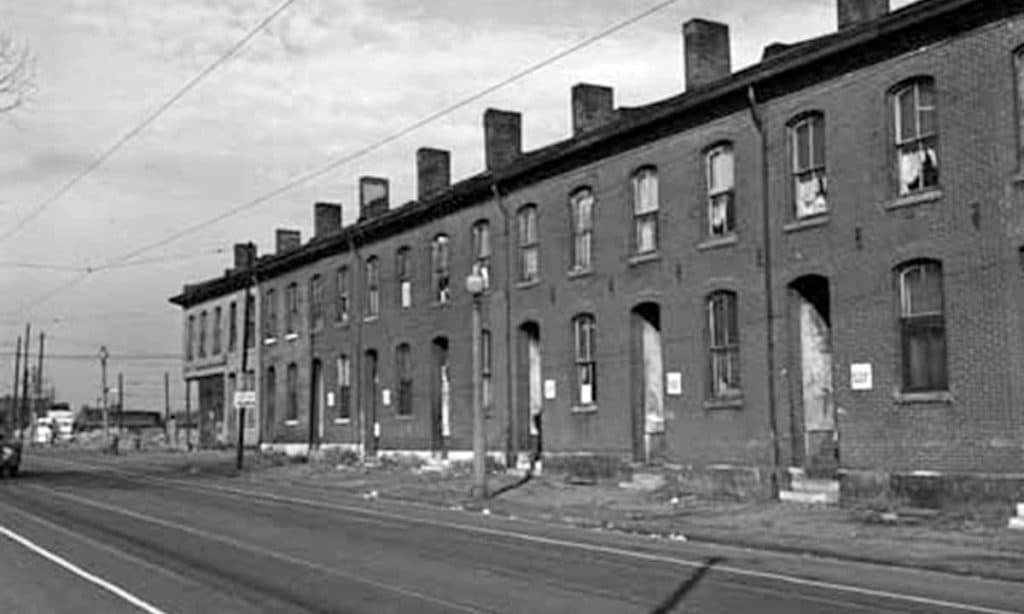
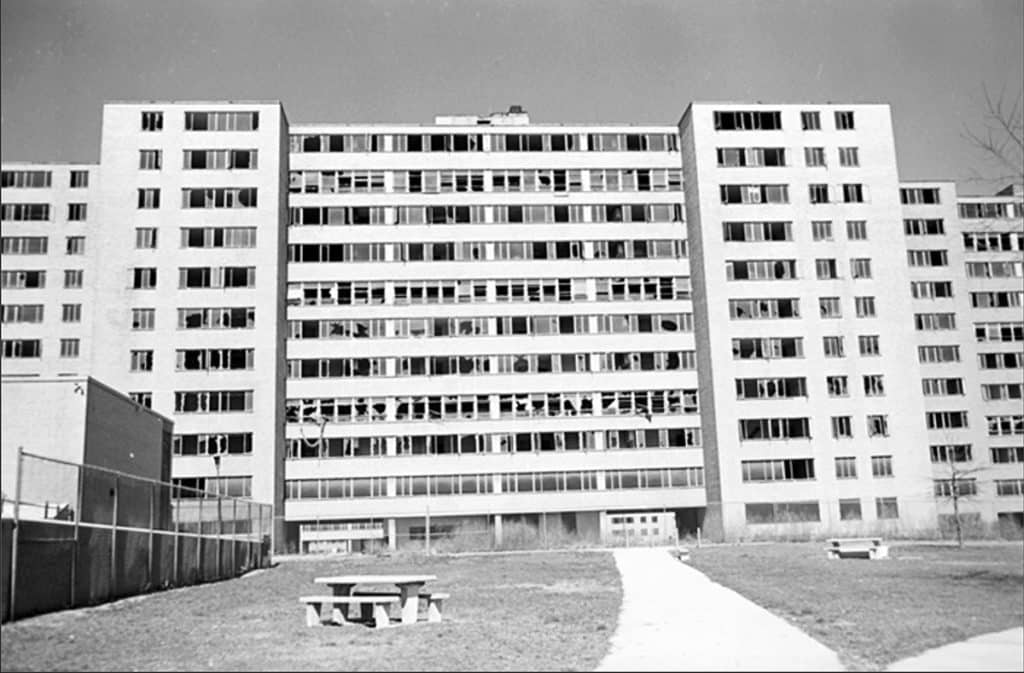
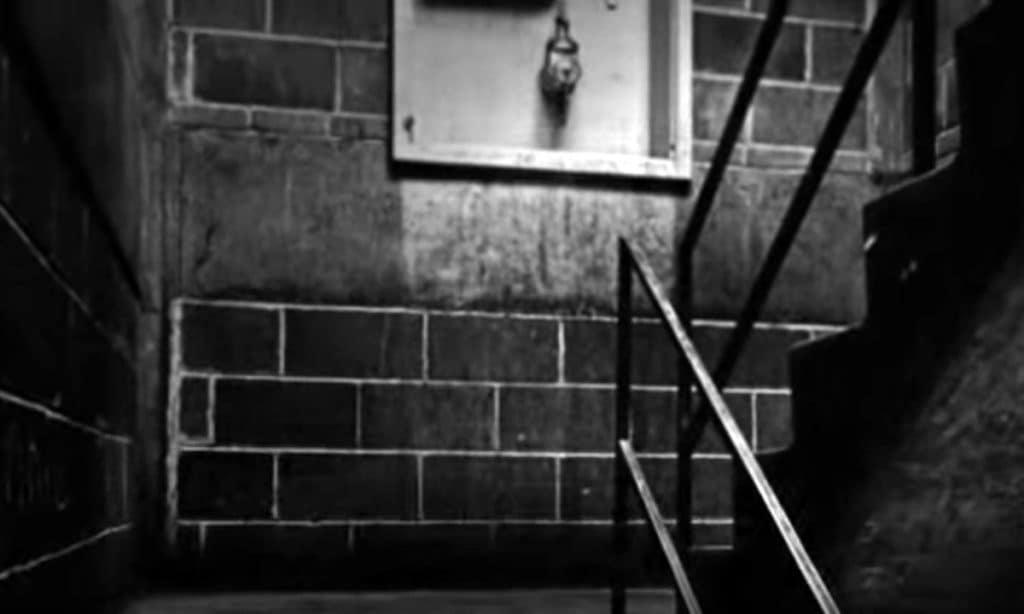
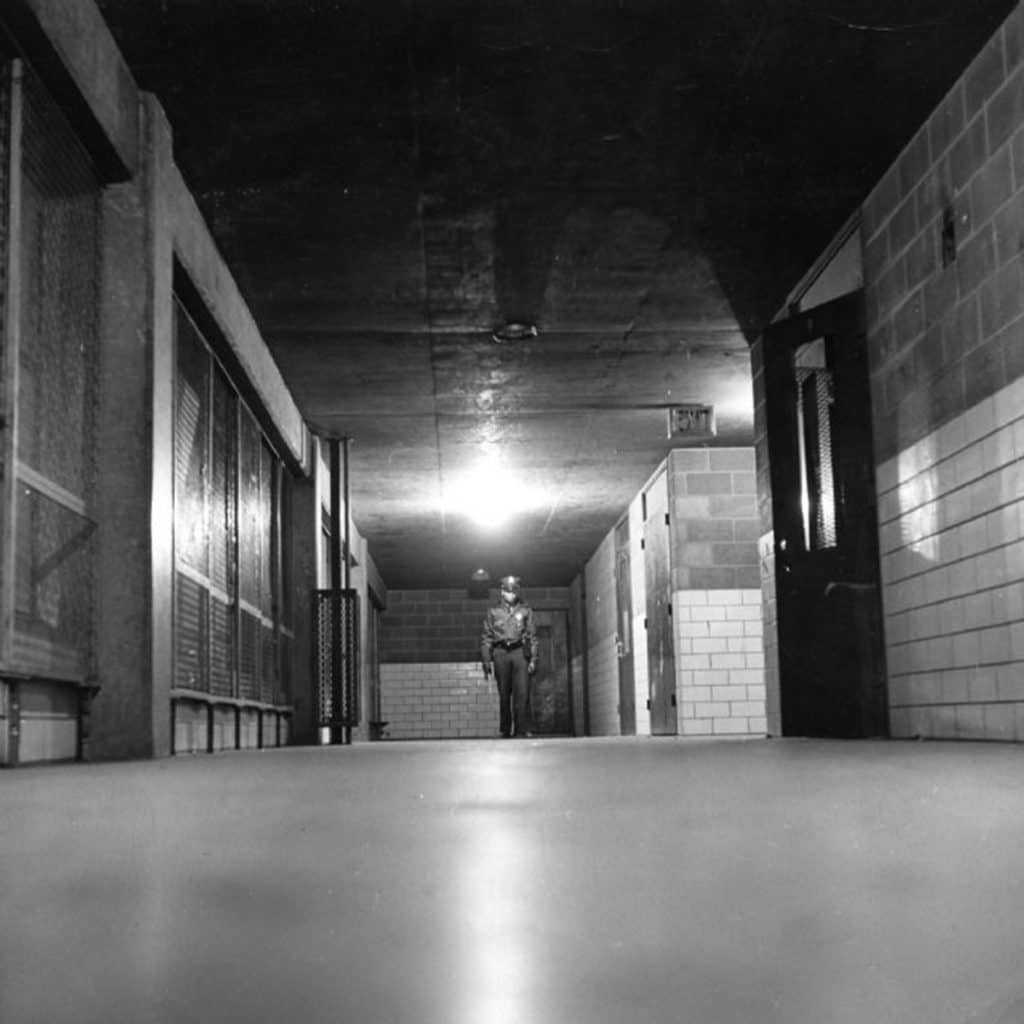









 People must have quickly realized the opportunities inherent in the design and planning of the pilotis feature because intensive patrols of the buildings and grounds began shortly after Pruitt-Igoe opened, even before any welfare recipients were allowed to live there. Former residents indicate these stairwells/elevators were problematic spaces from the very beginning (Photograph:
People must have quickly realized the opportunities inherent in the design and planning of the pilotis feature because intensive patrols of the buildings and grounds began shortly after Pruitt-Igoe opened, even before any welfare recipients were allowed to live there. Former residents indicate these stairwells/elevators were problematic spaces from the very beginning (Photograph: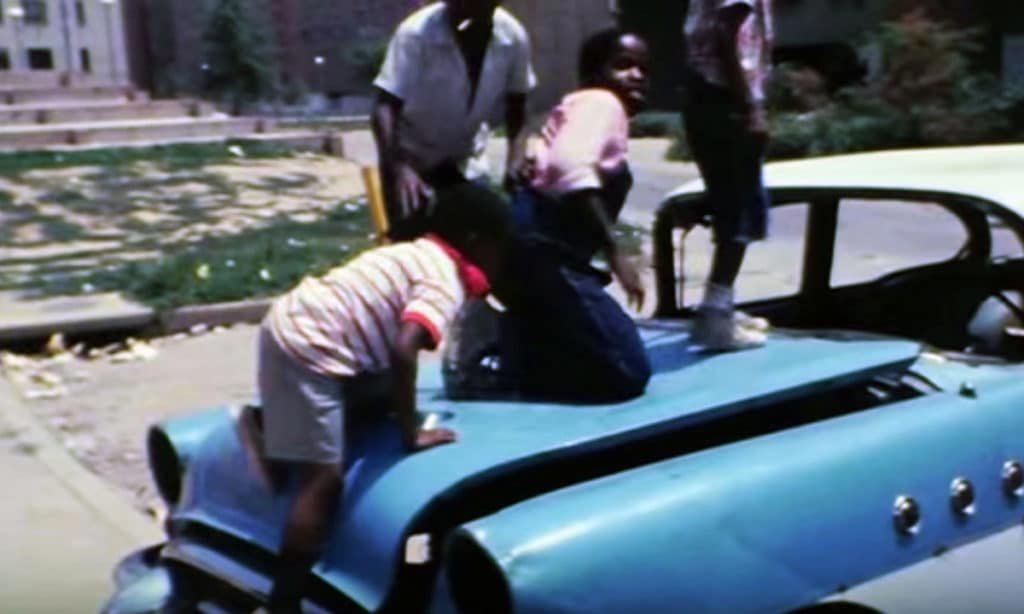 
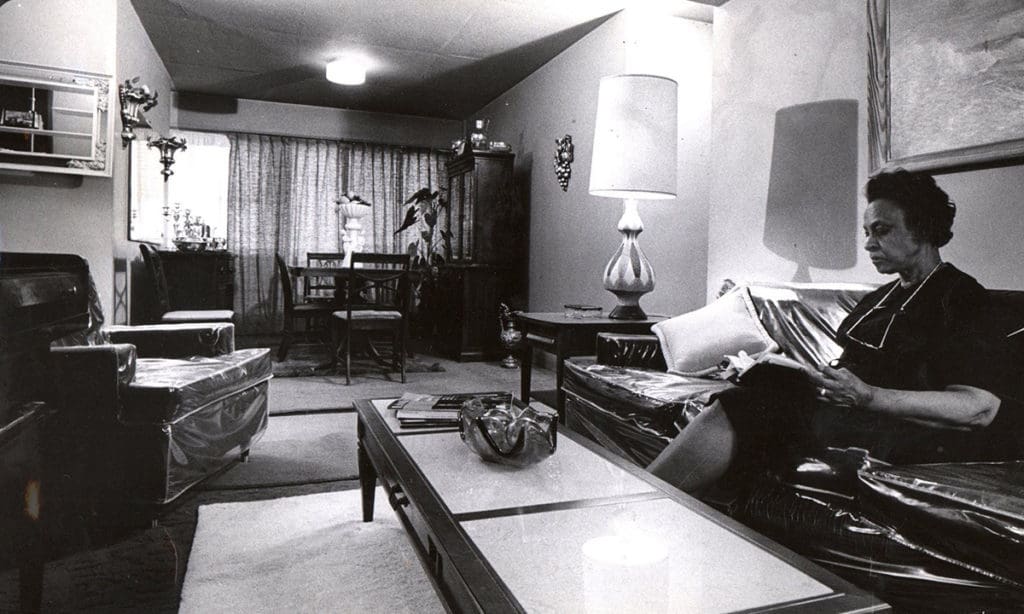 Social malaise accelerated at Pruitt-Igoe during the 1960s even as residents maintained some apartment interiors until a cataclysmic mechanical failure in 1968 (watch a 5-minute KMOX news report on YouTube
Social malaise accelerated at Pruitt-Igoe during the 1960s even as residents maintained some apartment interiors until a cataclysmic mechanical failure in 1968 (watch a 5-minute KMOX news report on YouTube 
 The course series reviewed dozens of examples in film and television. The question naturally arises about what might be the most definitive examples of architecture’s impact on cinema. What is the essential ‘must-see’ list of films for architects and planners to see?
The course series reviewed dozens of examples in film and television. The question naturally arises about what might be the most definitive examples of architecture’s impact on cinema. What is the essential ‘must-see’ list of films for architects and planners to see?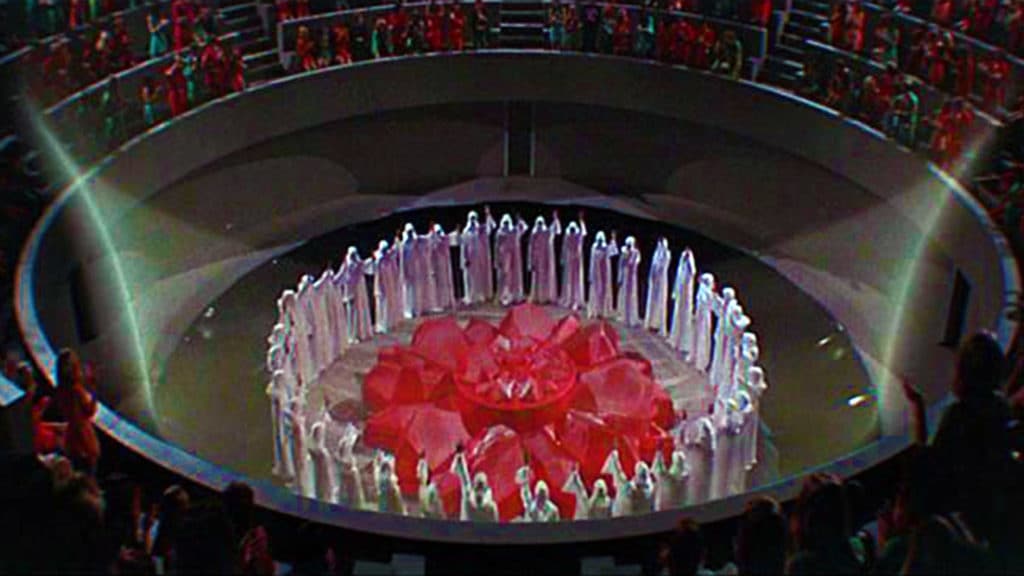
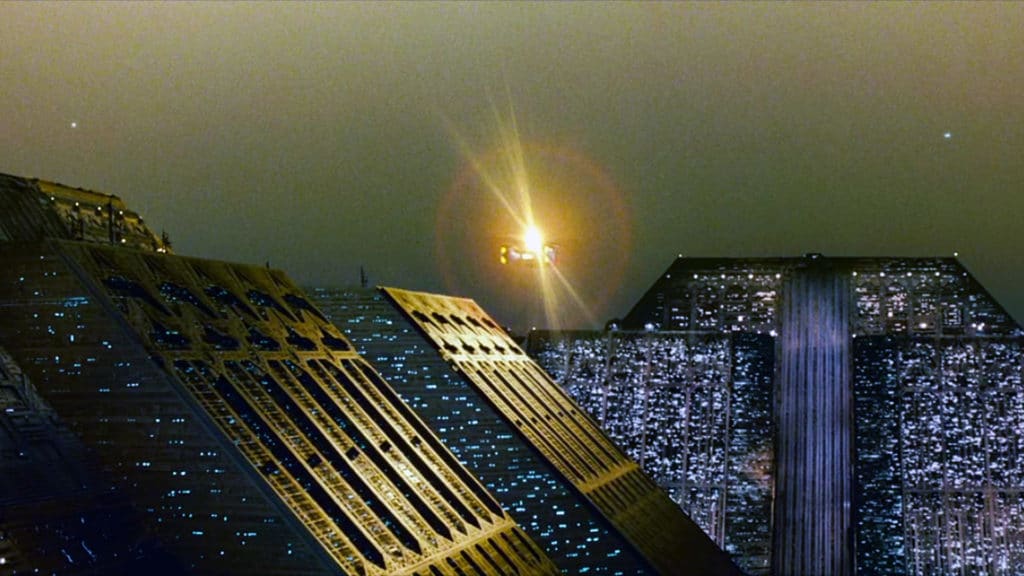
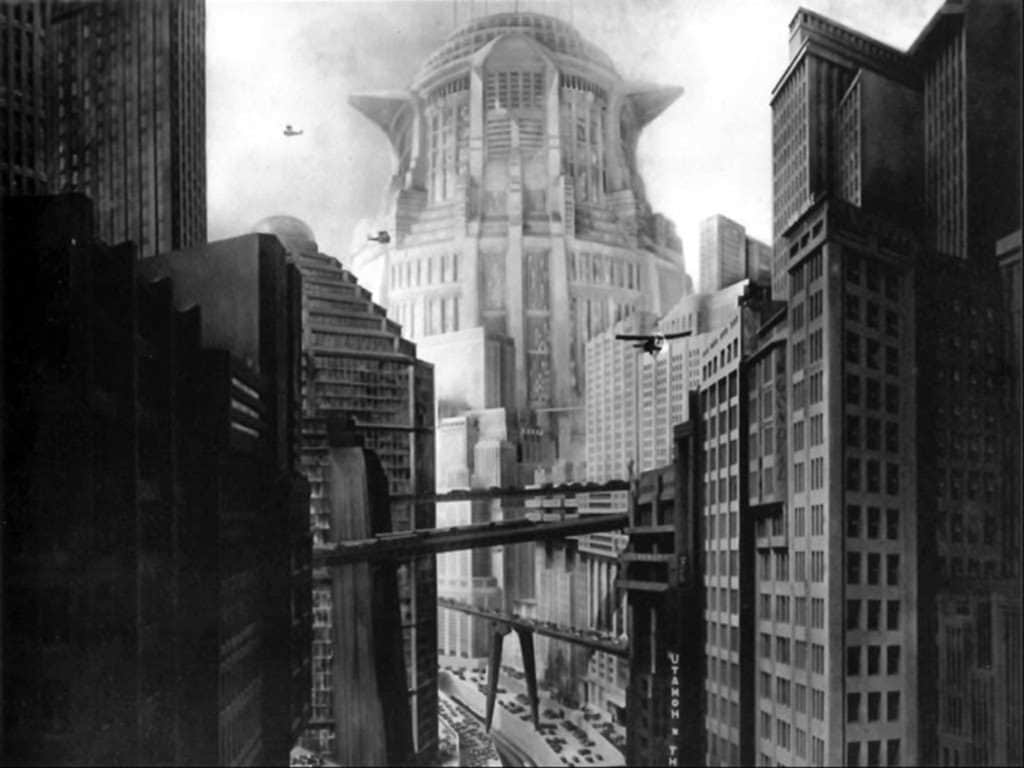


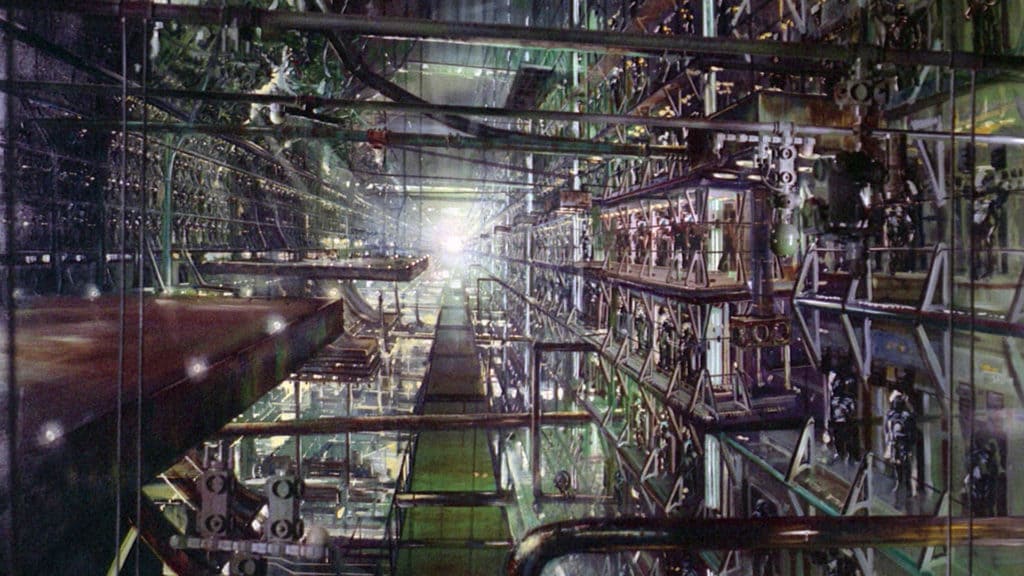




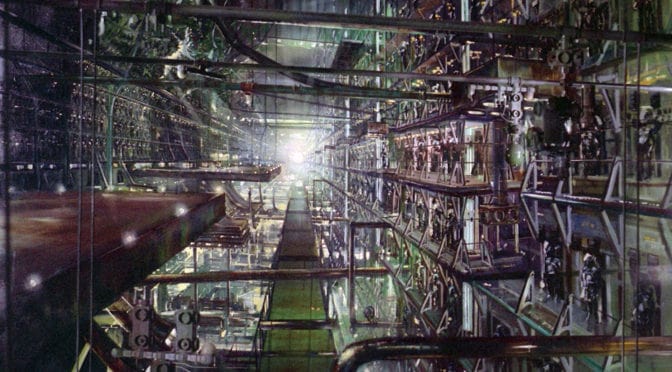
 1. Metropolis (1927)
1. Metropolis (1927)
 The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (6.0 course). Click
The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (6.0 course). Click 
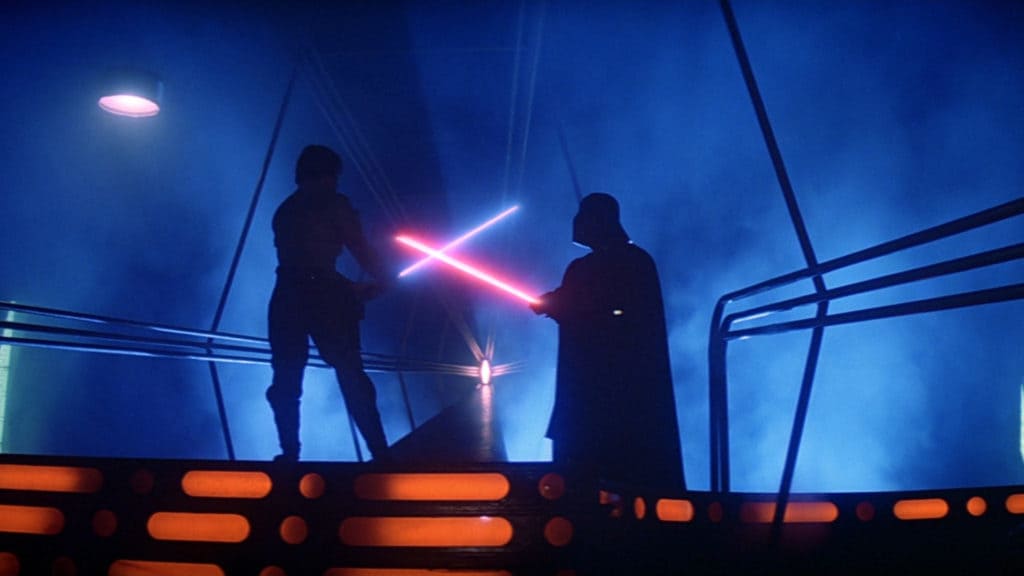
 Part III reviews the cinematic use of architectural precedents and typologies in crafting distinctive film-grammars in support of narrative and characterization for extended narratives. The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (2.0 hour course). Click
Part III reviews the cinematic use of architectural precedents and typologies in crafting distinctive film-grammars in support of narrative and characterization for extended narratives. The “Architecture and Film” course series more closely examines the frequent role of the built environment in creatively reinforcing or subverting expectations of the audience about cinematic narratives (2.0 hour course). Click