RE-POST | 20 Must-Read Texts for Urban Planners (#11-20)
by Dr. Mark David Major, AICP, CNU-A
(Originally posted January 22, 2013)
Lists are often a handy tool to spark a discussion, debate, or even an argument. The purpose of this list is pretty straightforward, i.e. what should you have read. Of course, in limiting the list to a mere 20 texts (books and articles), there is no possible way it can be exhaustive. There are a lot of interesting texts out there from a lot of different perspectives (some better than others). It is also true that compiling such a list will inevitably reveal the particular biases of the person preparing the compilation (like revealing your iTunes playlist). In the end, it is only their opinion.  There’s no way around it. This list demonstrates a clear bias towards texts about the relationship between the physical fabric of cities and their spatio-functional nature with a particular emphasis on first-hand observation of how things really work. Because of this, perhaps the most surprising thing about this list is how few texts there are by people who identify themselves as planners (or perhaps not, depending on your perspective). Finally, as with most lists, it is wise to reserve the right to amend/update said list in order to allow for any unfortunate oversights. Having said that, the list is an absolute good. The list is life. All around its margins lies suburban sprawl. Let the making of lists begin…
There’s no way around it. This list demonstrates a clear bias towards texts about the relationship between the physical fabric of cities and their spatio-functional nature with a particular emphasis on first-hand observation of how things really work. Because of this, perhaps the most surprising thing about this list is how few texts there are by people who identify themselves as planners (or perhaps not, depending on your perspective). Finally, as with most lists, it is wise to reserve the right to amend/update said list in order to allow for any unfortunate oversights. Having said that, the list is an absolute good. The list is life. All around its margins lies suburban sprawl. Let the making of lists begin…
 20. Learning from Las Vegas: The Forgotten Symbolism of Architectural Form (1972) by Robert Venturi, Steven Izenour and Denise Scott Brown
20. Learning from Las Vegas: The Forgotten Symbolism of Architectural Form (1972) by Robert Venturi, Steven Izenour and Denise Scott Brown
Venturi et al expand the arguments first outlined in Complexity and Contradiction in Architecture in 1966 to the urban level with their seminal study of Las Vegas. Only on these terms, it is an interesting read. However, dig a little deeper beneath the surface and into their wonderful series of figure-ground representations of spatial functioning on, along and adjacent to the Las Vegas Strip. You will discover Venturi et al concede – almost casually – the functional dynamics of how the strip operates to the realm of urban space and pattern in order to quickly focus on their arguments on what really interests them, i.e. the semantic nature of architectural form. A surface reading of only what Venturi et al writes misses a lot of the richness found within since there is a whole other book hidden based on what they are not saying but merely showing you. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 19. The Concept of Dwelling: on the way to figurative architecture (1985) by Christian Norberg-Schulz
19. The Concept of Dwelling: on the way to figurative architecture (1985) by Christian Norberg-Schulz
One always has to be careful with phenomenology because, by definition, almost everything written is subjective and open to vast differences in interpretation. However, much like the previous entry on this list, if a reader is willing to dig beneath of the surface and give thoughtful consideration about what, at first, appears to be purposefully opaque writing, then often there are rich rewards to be discovered. Norberg-Schulz’s The Concept of Dwelling is one of the best examples. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 18. Ladders, Architecture at Rice 34 (1996) by Albert Pope
18. Ladders, Architecture at Rice 34 (1996) by Albert Pope
It is something of a mystery why this book seems to be sorely under-appreciated and underrated outside of Houston, Texas. Pope’s study about the physical pattern of the American urban fabric is a fascinating read. Urban planners – especially American ones – could do a lot worse than read an entire book examining the physical pattern of the urban fabric in cities they are suppose to be planning; in fact, they have and do so regularly. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 17. Dreaming the Rational City: The Myth of American City Planning (1983) by M. Christine Boyer
17. Dreaming the Rational City: The Myth of American City Planning (1983) by M. Christine Boyer
Boyer’s The City of Collective Memory seems to overshadow her earlier book, which is a shame. Her history of the planning profession in the United States is a devastating and powerful critique that is as relevant today as when it was first published. It is also a much better book than The City of Collective Memory. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 16. America (1988) by Jean Baudrillard
16. America (1988) by Jean Baudrillard
The best planners are good sociologists and the best sociologists are great observers. Baudrillard was one of the best and keenest observers of human society and its meaning. Baudrillard wraps his observations within a flamboyant, often elegant, and occasionally beautiful use of language. It is not always clear whether the flurries of linguistic gymnastics are really his or is the result of translating from French into English. However, the results often amount to genius. In America, Baudrillard’s compare and contrast of Paris, New York, and Los Angeles yields rich rewards to any planner who dares to pay attention. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 15. Streets and Patterns (2005) by Stephen Marshall
15. Streets and Patterns (2005) by Stephen Marshall
The first half of Marshall’s book is a brilliant review and analysis of where we are and how we got here. The second half – focusing on possible solutions – descends into being only interesting. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 14. City: Rediscovering the Center (1989) by William H. Whyte
14. City: Rediscovering the Center (1989) by William H. Whyte
Whyte’s study of informal, social interaction in public spaces is a case study in urban observation that any planner should seek to take into account and emulate. Yes, sometimes Whyte’s conclusions are too localized about the attributes of the space itself than how it fits into the pattern of a larger urban context. However, at other times, his findings are remarkable for their common sense. For example, people in public spaces will move chairs for the purpose of promoting interaction rather than locate their interactions where chairs are located or tend to locate social interaction in areas of high movement like street corners. Anyone who has ever tried to move their way through to party – mumbling to themselves “why do people have to stop here to talk” – will understand many of Whyte’s observations about human nature and informal interaction are rock solid. Whyte’s City can almost be read as a companion piece to Jane Jacobs’ The Death and Life of Great American Cities. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
 13. “The Architecture of Community: Some New Proposals on the Social Consequences of Architectural and Planning Decisions” (1987) by Julienne Hanson and Bill Hillier, Architecture and Comportement, Architecture and Behaviour, 3(3): 251-273.
13. “The Architecture of Community: Some New Proposals on the Social Consequences of Architectural and Planning Decisions” (1987) by Julienne Hanson and Bill Hillier, Architecture and Comportement, Architecture and Behaviour, 3(3): 251-273.
There are many texts by a lot of people about why space syntax is important. However, few have driven home the point more powerfully and succinctly than this early article by Hanson and Hillier about the social consequences of design decisions for Modern housing estates (projects) in the UK. In doing so, Hanson and Hillier add considerable intellectual and quantitative heft to Jane Jacobs’ arguments about urban safety and “eyes on the street” in The Death and Life of Great American Cities. This article will probably be obscure to most planners, especially in the USA. The real crime is it’s rarely read outside of the space syntax community itself. Download the article here.
 12. Suburban Nation: The Rise of Sprawl and the Decline of the American Dream (2000) by Andres Duany, Elizabeth Plater-Zyberk and Jeff Speck
12. Suburban Nation: The Rise of Sprawl and the Decline of the American Dream (2000) by Andres Duany, Elizabeth Plater-Zyberk and Jeff Speck
A purist will probably argue when it comes to New Urbanism, start with The New Urbanism by Peter Katz. If you’re not really keen on appetizers, then go straight to the main meal. Suburban Nation is not only about what is the New Urbanism but also delves into the argument about why we need the New Urbanism today. New Urbanism does not always get it right. Does anybody? However, there shouldn’t be any doubt that it is heading in the right direction and that is a huge achievement in itself. Click here to purchase on Amazon.
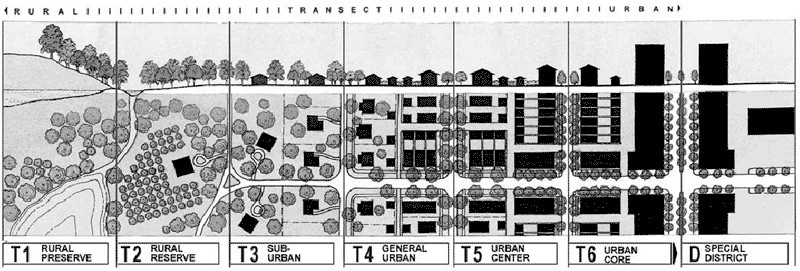 11. “Transect Planning” (2002) by Andres Duany and Emily E. Talen. APA Journal, 68(3): 245-266.
11. “Transect Planning” (2002) by Andres Duany and Emily E. Talen. APA Journal, 68(3): 245-266.
Duany and Talen elegantly translate a fundamental aspect about the spatio-functioning of streets tailored to urban form into understandable terms for public officials, urban designers and planners who are still trapped in – or refuse to leave – the box of the Euclidean zoning model and the arbitrary roadway classifications almost universally associated with it over the last half-century. In terms of the prevailing planning paradigm afflicting our cities, transect planning is the metaphorical equivalent of Duany and Talen pushing a Trojan horse inside the city gates. The more applied, the less tenable becomes the roadway classifications associated with the Euclidean zoning model. Beware of New Urbanists bearing gifts (i.e. methodology). You can read the abstract here.
Read Top 20 ‘Must-Read’ Texts for Urban Planners (#1-10) here!
 However, in more important ways, American cities are still subject to the same processes linking street networks and human use found in all cities of the world.
However, in more important ways, American cities are still subject to the same processes linking street networks and human use found in all cities of the world.


 There’s no way around it. This list demonstrates a clear bias towards texts about the relationship between the physical fabric of cities and their spatio-functional nature with a particular emphasis on first-hand observation of how things really work. Because of this, perhaps the most surprising thing about this list is how few texts there are by people who identify themselves as planners (or perhaps not, depending on your perspective). Finally, as with most lists, it is wise to reserve the right to amend/update said list in order to allow for any unfortunate oversights. Having said that, the list is an absolute good. The list is life. All around its margins lies suburban sprawl. Let the making of lists begin…
There’s no way around it. This list demonstrates a clear bias towards texts about the relationship between the physical fabric of cities and their spatio-functional nature with a particular emphasis on first-hand observation of how things really work. Because of this, perhaps the most surprising thing about this list is how few texts there are by people who identify themselves as planners (or perhaps not, depending on your perspective). Finally, as with most lists, it is wise to reserve the right to amend/update said list in order to allow for any unfortunate oversights. Having said that, the list is an absolute good. The list is life. All around its margins lies suburban sprawl. Let the making of lists begin…










 and 3) the consequences of government regulations, Euclidean zoning, modern transportation planning, and suburbanization during the post-war period in generating a hierarchal grid logic to the American regular grid planning tradition. The implications of development patterns and land consumption unseen during the history of city building over the previous 10,000 years are discussed.
and 3) the consequences of government regulations, Euclidean zoning, modern transportation planning, and suburbanization during the post-war period in generating a hierarchal grid logic to the American regular grid planning tradition. The implications of development patterns and land consumption unseen during the history of city building over the previous 10,000 years are discussed.
 By understanding these concepts, we can better understand how “bedrock” urban attributes (such as block size and dwelling entrances) and common growth trends (such as strip malls and leapfrog development) play a role in the spatial logic of American cities. The objective of this course is to better understand the spatial implications of design decisions when intervening in the American city.
By understanding these concepts, we can better understand how “bedrock” urban attributes (such as block size and dwelling entrances) and common growth trends (such as strip malls and leapfrog development) play a role in the spatial logic of American cities. The objective of this course is to better understand the spatial implications of design decisions when intervening in the American city.
 The course also compares the characteristics of block and street length in several American and European cities to demonstrate how Americans used the regular grid to build on a massive scale in the horizontal dimension of the city, which suburban sprawl has accentuated and abused since World War II. Finally, the course also discusses implications for sustainable cities in the 21st century.
The course also compares the characteristics of block and street length in several American and European cities to demonstrate how Americans used the regular grid to build on a massive scale in the horizontal dimension of the city, which suburban sprawl has accentuated and abused since World War II. Finally, the course also discusses implications for sustainable cities in the 21st century.